Difference between revisions of "User:Tohline/H BookTiledMenu"
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
==Spherically Symmetric Configurations== | ==Spherically Symmetric Configurations== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="float:right; margin-left: 300px; border-style: solid; border-width: 2px; border=color:black;" | |||
|- | |||
! style="height: 150px; width: 150px;"|[[User:Tohline/SphericallySymmetricConfigurations/Virial#Structural_Form_Factors|Structural<br />Form<br />Factors]] | |||
| | |||
! style="height: 150px; width: 150px; background-color:#9390DB; border-left:2px solid black;"|[[User:Tohline/SphericallySymmetricConfigurations/Virial#Free_Energy_Expression|Free Energy<br />of<br />Spherical<br />Systems]] | |||
|} | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="margin-right: auto; margin-left: 0px; border-style: solid; border-width: 2px border-color: black;" | {| class="wikitable" style="margin-right: auto; margin-left: 0px; border-style: solid; border-width: 2px border-color: black;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 22:33, 6 August 2017
Tiled Menu

|
|---|
| | Tiled Menu | Tables of Content | Banner Video | Tohline Home Page | |
Context
| Global Energy Considerations |
|---|
| Principal Governing Equations (PGEs) |
Continuity | Euler | 1st Law of Thermodynamics |
Poisson |
|---|
| Equation of State (EOS) |
Total Pressure |
|---|
Spherically Symmetric Configurations
| Structural Form Factors |
Free Energy of Spherical Systems |
|---|
| One-Dimensional PGEs |
|---|
Equilibrium Structures
| Hydrostatic Balance Equation |
Solution Strategies |
|---|
| Isothermal Sphere |
via Direct Numerical Integration |
|---|
| Isolated Polytropes |
Known Analytic Solutions |
via Direct Numerical Integration |
via Self-Consistent Field (SCF) Technique |
|---|
| Zero-Temperature White Dwarf |
Chandrasekhar Limiting Mass (1935) |
|---|
| Pressure-Truncated Configurations |
Bonnor-Ebert (Isothermal) Spheres (1955 - 56) |
Polytropes | Equilibrium Sequence Turning-Points |
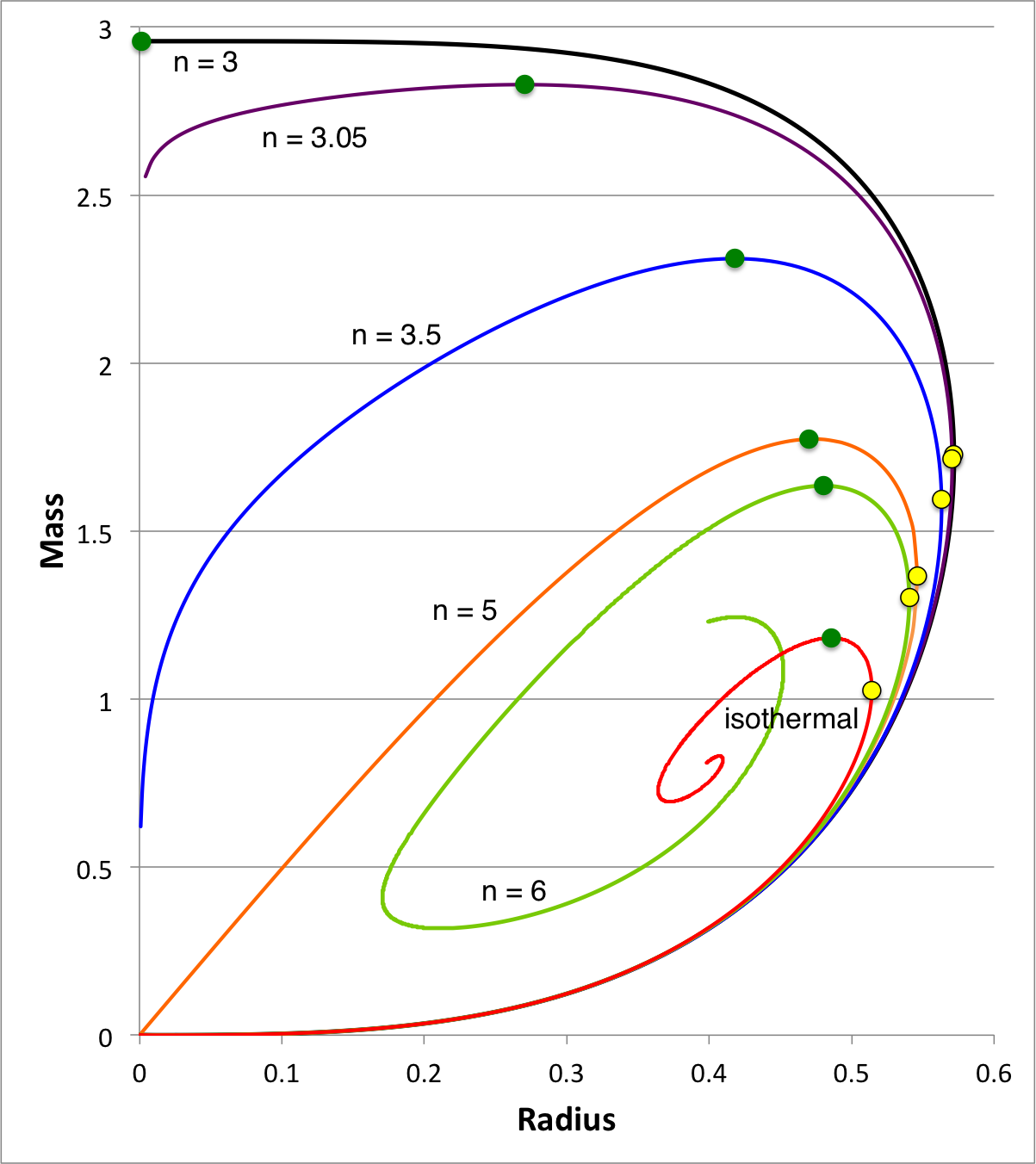
|
|---|
Stability Analysis
| Radial Pulsation Equation |
Example Derivations & Statement of Eigenvalue Problem |
Relationship to Sound Waves |
|---|
| Uniform-Density Configurations |
Sterne's Analytic Sol'n of Eigenvalue Problem (1937) |
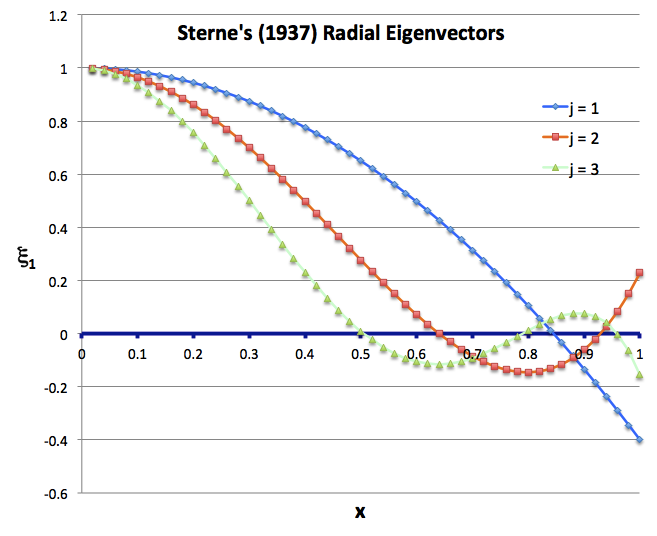
|
|---|
| Pressure-Truncated Isothermal Spheres |
|
via Direct Numerical Integration |
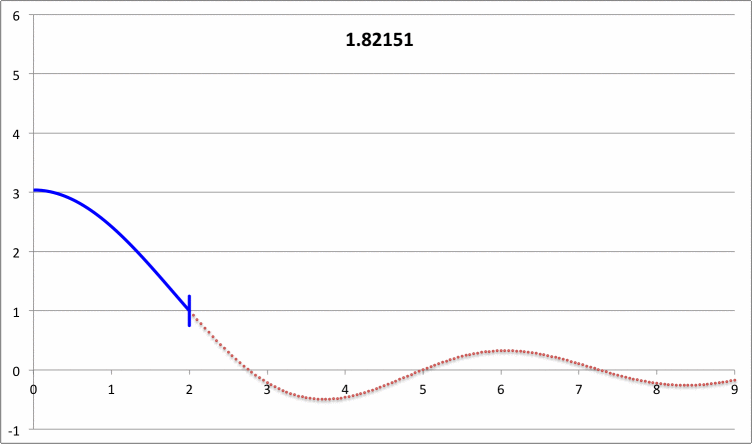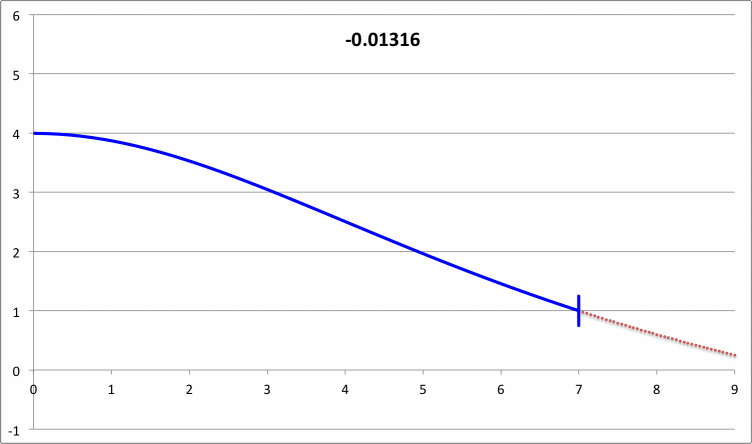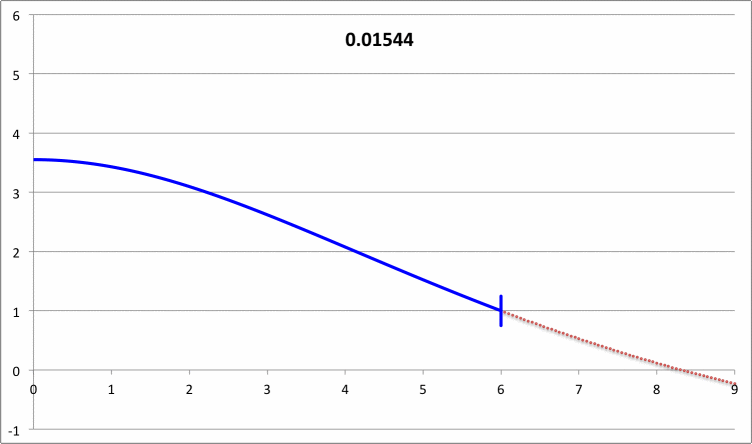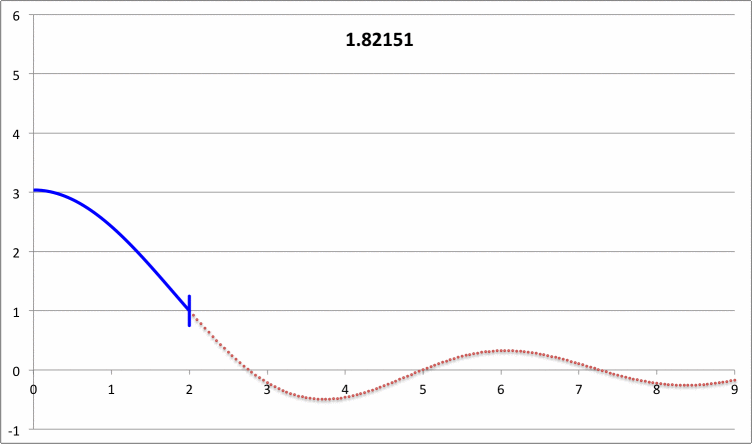
| |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yabushita's Analytic Sol'n for Marginally Unstable Configurations (1974) |
|
|---|
| Polytropes |
|
Isolated n = 3 Polytrope |
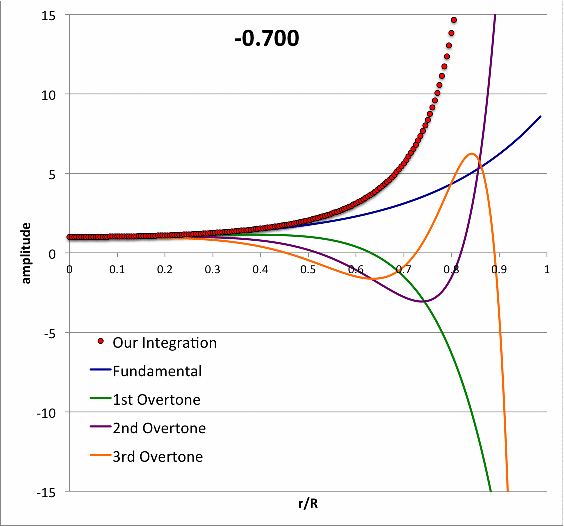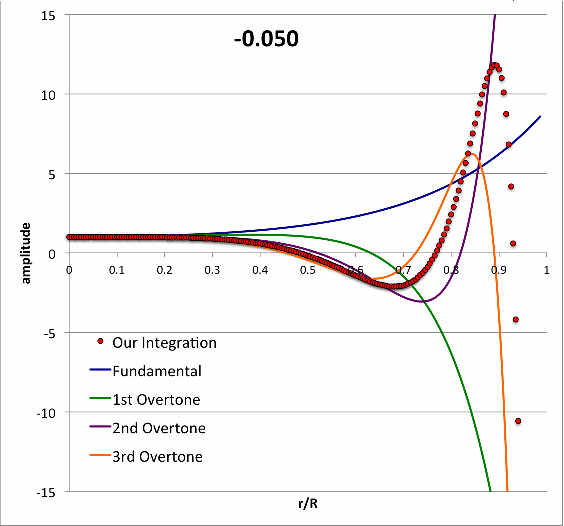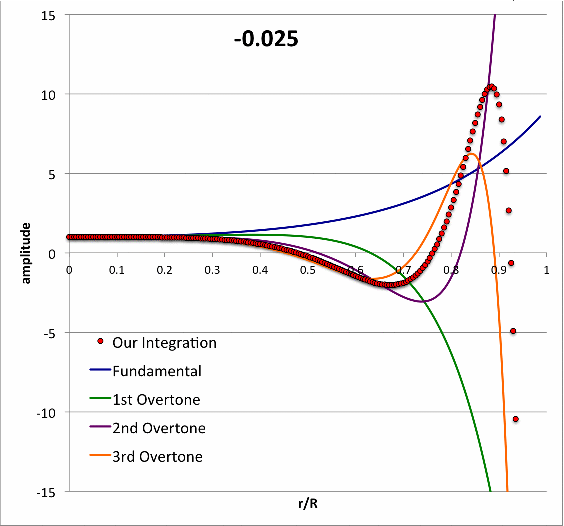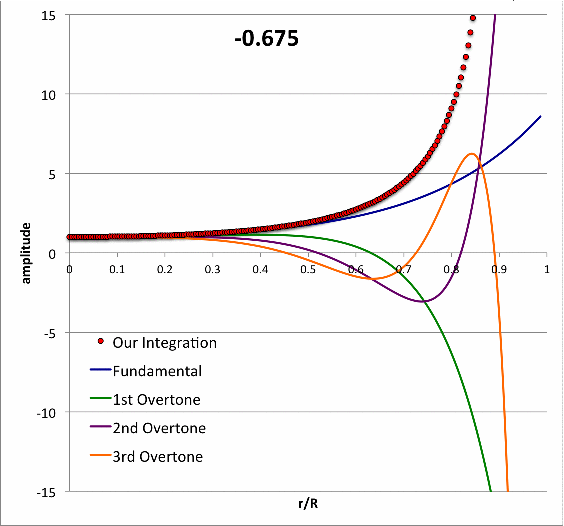
|
Pressure-Truncated Configurations | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Our Analytic Sol'n for Marginally Unstable Configurations (2017) |
|
|---|
Nonlinear Dynamical Evolution
| Free-Fall Collapse |
|---|
| Collapse of Isothermal Spheres |
via Direct Numerical Integration |
Similarity Solution |
|---|
| Collapse of an Isolated n = 3 Polytrope |
|---|
See Also

|
|---|
|
© 2014 - 2021 by Joel E. Tohline |


