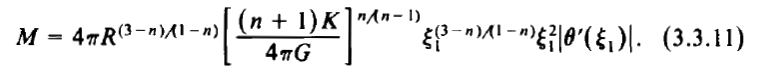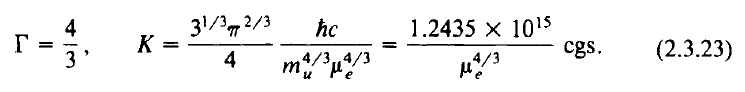User:Tohline/SSC/Structure/WhiteDwarfs
White Dwarfs

|
|---|
| | Tiled Menu | Tables of Content | Banner Video | Tohline Home Page | |
Mass-Radius Relationships
The following summaries are drawn from Appendix A of Even & Tohline (2009).
Chandrasekhar mass
Chandrasekhar (1935) was the first to construct models of spherically symmetric stars using the barotropic equation of state appropriate for a degenerate electron gas, namely,
|
<math>~P_\mathrm{deg} = A_\mathrm{F} F(\chi) </math> |
|
|
where: <math>F(\chi) \equiv \chi(2\chi^2 - 3)(\chi^2 + 1)^{1/2} + 3\sinh^{-1}\chi</math> |
|
|
and: |
<math>\chi \equiv (\rho/B_\mathrm{F})^{1/3}</math> |
In so doing, he demonstrated that the maximum mass of an isolated, nonrotating white dwarf is <math>M_\mathrm{Ch} = 1.44 (\mu_e/2)M_\odot</math>, where <math>~\mu_e</math> is the number of nucleons per electron and, hence, depends on the chemical composition of the white dwarf. A concise derivation of <math>M_\mathrm{Ch}</math> (although, at the time, it was referred to as <math>M_3</math>) is presented in Chapter XI of Chandrasekhar (1967), where we also find the expressions for the characteristic Fermi pressure, <math>~A_\mathrm{F}</math>, and the characteristic Fermi density, <math>~B_\mathrm{F}</math>. The derived analytic expression for the limiting mass is,
<math>\mu_e^2 M_\mathrm{Ch} = 4\pi m_3 \biggl( \frac{2A_\mathrm{F}}{\pi G} \biggr)^{3/2} \frac{\mu_e^2}{B_\mathrm{F}^2} = 1.14205\times 10^{34} ~\mathrm{g}</math>,
where the coefficient,
<math>m_3 \equiv \biggl(-\xi^2 \frac{d\theta_3}{d\xi} \biggr)_\mathrm{\xi=\xi_1(\theta_3)} = 2.01824</math>,
represents a structural property of <math>n = 3</math> polytropes (<math>\gamma = 4/3</math> gasses) whose numerical value can be found in Chapter IV, Table 4 of Chandrasekhar (1967). We note as well that Chandrasekhar (1967) identified a characteristic radius, <math>\ell_1</math>, for white dwarfs given by the expression,
<math> \ell_1 \mu_e \equiv \biggl( \frac{2A_\mathrm{F}}{\pi G} \biggr)^{1/2} \frac{\mu_e}{B_\mathrm{F}} = 7.71395\times 10^8~\mathrm{cm} . </math>
The Nauenberg Mass-Radius Relationship
Nauenberg (1972) derived an analytic approximation for the mass-radius relationship exhibited by isolated, spherical white dwarfs that obey the zero-temperature white-dwarf equation of state. Specifically, he offered an expression of the form,
<math> R = R_0 \biggl[ \frac{(1 - n^{4/3})^{1/2}}{n^{1/3}} \biggr] , </math>
where,
|
<math> n </math> |
<math> \equiv </math> |
<math> \frac{M}{(\bar{\mu} m_u) N_0} , </math> |
|
<math> N_0 </math> |
<math> \equiv </math> |
<math> \frac{(3\pi^2\zeta)^{1/2}}{\nu^{3/2}} \biggl[ \frac{hc}{2\pi G(\bar\mu m_u)^2} \biggr]^{3/2} = \frac{\mu_e^2 m_p^2}{(\bar\mu m_u)^3} \biggl[ \frac{4\pi \zeta}{m_3^2 \nu^3} \biggr]^{1/2} M_\mathrm{Ch} , </math> |
|
<math> R_0 </math> |
<math> \equiv </math> |
<math> (3\pi^2 \zeta)^{1/3} \biggl[ \frac{h}{2\pi m_e c} \biggr] N_0^{1/3} = \frac{\mu_e m_p}{\bar\mu m_u} \biggl[ \frac{4\pi \zeta}{\nu} \biggr]^{1/2} \ell_1 , </math> |
<math>~m_u</math> is the atomic mass unit, <math>~\bar{\mu}</math> is the mean molecular weight of the gas, and <math>\zeta</math> and <math>\nu</math> are two adjustable parameters in Nauenberg's analytic approximation, both of which are expected to be of order unity. By assuming that the average particle mass denoted by Chandrasekhar (1967) as <math>(\mu_e m_p)</math> is identical to the average particle mass specified by Nauenberg (1972) as <math>(\bar\mu m_u)</math> and, following Nauenberg's lead, by setting <math>\nu = 1</math> and,
<math>\zeta = \frac{m_3^2}{4\pi} = 0.324142</math>,
in the above expression for <math>N_0</math>, we see that,
<math> (\bar\mu m_u)N_0 = M_\mathrm{Ch} . </math>
Hence, the denominator in the above expression for <math>n</math> becomes the Chandrasekhar mass. Furthermore, the above expressions for <math>R_0</math> and <math>R</math> become, respectively,
<math> \mu_e R_0 = m_3(\ell_1 \mu_e) = 1.55686\times 10^9~\mathrm{cm} , </math>
and,
<math> R = R_0 \biggl\{ \frac{[1 - (M/M_\mathrm{Ch})^{4/3} ]^{1/2}}{(M/M_\mathrm{Ch})^{1/3}} \biggr\} . </math>
Finally, by adopting appropriate values of <math>M_\odot</math> and <math>R_\odot</math>, we obtain essentially the identical approximate, analytic mass-radius relationship for zero-temperature white dwarfs presented in Eqs. (27) and (28) of Nauenberg (1972):
<math> \frac{R}{R_\odot} = \frac{0.0224}{\mu_e} \biggl\{ \frac{[1 - (M/M_\mathrm{Ch})^{4/3} ]^{1/2}}{(M/M_\mathrm{Ch})^{1/3}} \biggr\} , </math>
where,
<math> \frac{M_\mathrm{Ch}}{M_\odot} = \frac{5.742}{\mu_e^2} . </math>
Eggleton Mass-Radius Relationship
Verbunt & Rappaport (1988) introduced the following approximate, analytic expression for the mass-radius relationship of a "completely degenerate <math>\ldots</math> star composed of pure helium" (i.e., <math>\mu_e = 2</math>), attributing the expression's origin to Eggleton (private communication):
<math> \frac{R}{R_\odot} = 0.0114 \biggl[ \biggl(\frac{M}{M_\mathrm{Ch}}\biggr)^{-2/3} - \biggl(\frac{M}{M_\mathrm{Ch}}\biggr)^{2/3} \biggr]^{1/2} \biggl[ 1 + 3.5 \biggl(\frac{M}{M_p}\biggr)^{-2/3} + \biggl(\frac{M}{M_p}\biggr)^{-1} \biggr]^{-2/3} , </math>
where <math>M_p</math> is a constant whose numerical value is <math>0.00057 M_\odot</math>. This "Eggleton" mass-radius relationship has been used widely by researchers when modeling the evolution of semi-detached binary star systems in which the donor is a zero-temperature white dwarf. Since the Nauenberg (1972) mass-radius relationship discussed above is retrieved from this last expression in the limit <math>M/M_p \gg 1</math>, it seems clear that Eggleton's contribution was the insertion of the term in square brackets involving the ratio <math>M/M_p</math> which, as Marsh, Nelemans & Steeghs (2004) phrase it, "allows for the change to be a constant density configuration at low masses (Zapolsky & Salpeter 1969)."
Highlights from Discussion by Shapiro & Teukolsky (1983)
Here we interleave our own derivations and discussions with the presentation found in [ST83].
In our accompanying discussion, we have shown that the equilibrium radius of an isolated polytrope is given, quite generally, by the expression,
|
<math>~R_\mathrm{eq} </math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\biggl[\biggl(\frac{G}{K_n}\biggr)^n M_\mathrm{tot}^{n-1} \biggr]^{1/(n-3)} \biggl[ \frac{4\pi}{(n+1)^n} \biggr]^{1/(n-3)} \biggl[(-\theta^') \xi^2\biggr]_{\xi_1}^{(1-n)/(n-3)} \xi_1 \, . </math> |
Inverting this provides the following expression for the total mass in terms of the equilibrium radius:
|
<math>~ M_\mathrm{tot}^{1-n} </math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~R_\mathrm{eq}^{3-n}\biggl(\frac{G}{K_n}\biggr)^n \biggl[ \frac{4\pi}{(n+1)^n} \biggr] \biggl[(-\theta^') \xi^2\biggr]_{\xi_1}^{1-n} \xi_1^{n-3} </math> |
|
<math>~\Rightarrow~~~ M_\mathrm{tot}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~R_\mathrm{eq}^{(3-n)/(1-n)}\biggl[\frac{G}{(n+1)K_n}\biggr]^{n/(1-n)} ( 4\pi )^{1/(1-n)} \biggl[(-\theta^') \xi^2\biggr]_{\xi_1} \xi_1^{(n-3)/(1-n)} </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~4\pi R_\mathrm{eq}^{(3-n)/(1-n)}\biggl[\frac{(n+1)K_n}{4\pi G}\biggr]^{n/(n-1)} \biggl[(-\theta^') \xi^2\biggr]_{\xi_1} \xi_1^{(n-3)/(1-n)} </math> |
As is shown by the following boxed-in image, this expression matches equation (3.3.11) from [ST83], except for the sign of the exponent on <math>~\xi_1</math>, which is demonstratively correct in our expression.
|
Equation extracted from §3.3 (p. 63) of [ST83] |
Given that (see equation 3.3.12 of [ST83]) in the relativistic limit, <math>~\Gamma = \gamma_g = 4/3</math> — that is, <math>~n=3</math> — and acknowledging as we have above that, for isolated <math>~n = 3</math> polytropes,
<math>m_3 \equiv \biggl(-\xi^2 \frac{d\theta_3}{d\xi} \biggr)_\mathrm{\xi=\xi_1(\theta_3)} = 2.01824</math>,
|
Equation extracted from §3.3 (p. 63) of [ST83] |
this polytropic expression for the mass becomes,
|
<math>~ M_\mathrm{tot}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~4\pi m_3 \biggl[\frac{ K_3 }{\pi G}\biggr]^{3/2} \, . </math> |
Separately, [ST83] show that the effective polytropic constant for a relativistic electron gas is (see their equation 2.3.23),
|
<math>~K_3</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \biggl( \frac{3\pi^2}{2^6}\biggr)^{1/ 3} \biggl[ \frac{ \hbar^3 c^3 }{ m_u^4 \mu_3^4 } \biggr]^{ 1 / 3} = \biggl[ \frac{3 h^3 c^3 }{2^9\pi m_u^4 \mu_3^4 } \biggr]^{ 1 / 3} \, . </math> |
|
Equation extracted from §2.3 (p.27) of [ST83] |
Together, then, the [ST83] analysis gives,
|
<math>~ M_\mathrm{tot}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~4\pi m_3 \biggl[\frac{ 1 }{\pi G}\biggr]^{3/2} \biggl[ \frac{3 h^3 c^3 }{2^9\pi m_u^4 \mu_3^4 } \biggr]^{ 1 / 2} </math> |
And, given that,
|
<math>~</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~</math> |
<math>A_\mathrm{F} \equiv \frac{\pi m_e^4 c^5}{3h^3} </math>
<math>\frac{B_\mathrm{F}}{\mu_e} \equiv \frac{8\pi m_p}{3} \biggl( \frac{m_e c}{h} \biggr)^3 \, ,</math>
we have,
|
<math>~ M_\mathrm{tot}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~4\pi m_3 \biggl[\frac{ 2A_F }{\pi G}\biggr]^{3/2} \frac{\mu_e^2}{B_F^2} \biggl[ \frac{3 h^3 c^3 }{2^9\pi m_u^4 \mu_3^4 } \biggr]^{ 1 / 2} \biggl[ \frac{8\pi m_p}{3} \biggl( \frac{m_e c}{h} \biggr)^3 \biggr]^2 \biggl[\frac{3h^3}{2\pi m_e^4 c^5} \biggr]^{3 / 2} </math> |

|
|---|
|
© 2014 - 2021 by Joel E. Tohline |