SciVisFall2008/Schedule
8/26: Introduction to visualization
Lecturer: Claudio
Topics: Scientific Visualization
Notes: lec01-notes.pdf
Slides: intro
Animations: NCSA storm animation
Further reading:
(Optional reading) Provenance for Computational Tasks: A Survey
8/28: The visualization pipeline
Lecturer: Claudio
Topics: Procedural vs. Dataflow programming; Using Dataflow for the Vis Pipeline; Dataflow programming with VTK; Dataflow programming with VisTrails; python.
Notes: lec02-notes.pdf
Slides: lec02.pdf
Further reading:
(Optional reading) Provenance for Visualizations: Reproducibility and Beyond, C. Silva, J. Freire, and S. Callahan, IEEE Computing in Science and Engineering, 2008.
9/2: Modeling Data for Visualization
Lecturer: Claudio
Topics: Discrete vs continous data; Sampling and interpolation; Point vs triangulated data; Meshing data types; Regular vs irregular data; Tabular data; Vector and tensor fields
Notes: modeling data
Slides: processing.ppt
Further reading:
Surface Simplification Using Quadric Error Metrics
(Optional Reading) A Memory Insensitive Technique for Large Model Simplification
(Optional Reading) Quadric-based Simplification in any Dimension
9/4: Modeling Data for Visualization
Lecturer: Claudio
Topics: Geometry Processing: Reconstruction and meshing; Simplification; Smoothing; Other Filtering algorithms
Notes: modeling data
Slides: processing.ppt
Further reading:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Least_squares
(Optional Reading) Robust Moving Least-squares Fitting with Sharp Features
(Optional Reading) Optimal Bandwidth Selection for MLS Surfaces
9/9: Elementary Plotting Techniques
Lecturer: Claudio
Topics: Principles of Graph Construction
Notes: PlottingNotes.pdf
Slides: Plotting1.pdf
Further Reading: There is no required reading for this lecture. For those interested in more depth, the following books are very useful:
- The Elements of Graphing Data. William S. Cleveland, Hobart Press, 2nd Edition, 1994.
- Visualizing Data. William S. Cleveland, Hobart Press, 1993.
- The Visual Display of Quantitative Information. Edward R. Tufte, Graphics Press, 2001.
- Visual Explanations: Images and Quantities, Evidence and Narrative. Edward R. Tufte, Graphics Press, 2997.
9/11: Elementary Plotting Techniques
Lecturer: Claudio
Topics: Simple Plotting Methods: Dot Plots, Connected Symbol Plots, Scatter Plots, Histograms, Others. Advanced Plotting Methods: Multimodal, Higher Dimensional, Correlation, Uncertainty and Variation.
Notes: PlottingNotes.pdf
Slides: Plotting2.pdf
Vistrails: PlottingVistrails.zip - Unzip this file in the examples directory of your VisTrails installation and it will add the vistrails along with their data sets (in the data directory). If you don't have permission to write to this directory (CADE users), then unzip the file where you want. Just be aware that in this case the paths for the data files may not be correct for most vistrails and will need to be fixed before they will execute properly.
Further Reading: There is no required reading for this lecture. Some articles of interest:
9/16: Color and Human Perception
Lecturer: Claudio
Topics: Human vision system; Optical illusions
Slides: human-vision.pdf
Links:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eye
http://www.grand-illusions.com/gregory2.htm (also, see the related book: [1])
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Purkinje_effect
http://www.handprint.com/HP/WCL/color2.html
9/18: Color and Human Perception
Lecturer: Jens Krueger
Topics: Color Science; Color spaces; Color Blindness; Color maps; Tone mapping;
Slides: colorvision-jens.pdf
Links:
Further reading:
How Not to Lie with Visualization
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Opponent_process
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_models
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Absolute_color_space
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Additive_color
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Subtractive_color
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RGB_color_model
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SRGB_color_space
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CIE_XYZ_color_space
9/23: Math refresher
Lecturer: Carlos Scheidegger
Topics: Basic linear algebra; vectors; basic differential geometry (space curves, tangents, normals, surfaces); basic vector calculus (gradient, divergence, curl, gauss' theorem, green's theorem)
Links:
Further Reading:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vector_calculus
Appendix A of these notes might be useful: [2]
Two books that take a very accessible approach at vector calculus:
Div, Grad, Curl, and All That: An Informal Text on Vector Calculus
A Student's Guide to Maxwell's Equations
9/25 2D Visualization Techniques
Lecturer: Claudio
Topics: 2-D contours, marching quads, marching tris; Color mapping; height fields; NPR
Slides: pdf file
Notes: pdf file
Vistrails: zip file with ozone.vt and data asymptotic decider in 2d heightfields
Note: These vistrails use relative file paths so you don't need to change each of them individually to match your directory structure. Simply unzip the file to whichever location is more convenient. Then, inside VisTrails, open the VisTrails shell, type:
import os
os.chdir("c:/directory/where/you/unzipped/it")
This will change the directory so you should be able to just run the pipelines.
Further reading:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/iel5/4271943/4271944/04272091.pdf
http://www.jstor.org/stable/pdfplus/2683294.pdf
An Efficient Naturalness-Preserving Image-Recoloring Method for Dichromats
9/30: 2D Visualization Techniques
Lecturer: Jens Krueger and Claudio
Topics: 2-D vector fields, div, grad, curl in 2D; Steady vs Unsteady flows; Glyphs; 2-D streamlines, streaklines, pathlines
Slides: pdf file
Further reading:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Streamlines,_streaklines_and_pathlines
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euler's_method
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Runge-Kutta
Demos:
http://www.win.tue.nl/~vanwijk/ibfv/
http://www.javaview.de/demo/PaLIC.html
Vistrails: vistrail with steady vector field vis and data vistrail with unsteady vector field vis and data Note: Because VTK does not support time-varying datasets directly, we had to create a reasonably ugly hack to simulate unsteady fields. This means the datasets are quite big (80MB in total).
"The Dx9 Particle Engine" as well as a few datasets
10/2: Volume Vis
Lecturer: Carlos
Topics: Slicing; Contours; Marching algorithms
Slides: iso-basic.pdf
References:
Marching cubes: A high resolution 3D surface construction algorithm
The asymptotic decider: resolving the ambiguity in marching cubes
10/2: Volume Vis
Lecturer: Carlos
Topics: Accelerating structures; High-quality contours
Slides:
References:
A Near Optimal Isosurface Extraction Algorithm Using the Span Space
Automatic Isosurface Propagation Using an Extrema Graph and Sorted Boundary Cell Lists
Speeding Up Isosurface Extraction Using Interval Trees
10/9: Volume Vis
Lecturer: Carlos Scheidegger
Topics: High quality isosurfaces
Slides: iso-quality.pdf
References:
Edge Transformations for Improving Mesh Quality of Marching Cubes
High-Quality Extraction of Isosurfaces from Regular and Irregular Grids
Dual contouring of hermite data
Topology, Accuracy, and Quality of Isosurface Meshes Using Dynamic Particles
Material interface reconstruction
10/14: Fall break
10/16: Fall break
10/21: Direct Volume Rendering
Lecturer: Huy Vo
Topics: Introduction to volume rendering
Slides: VolumeRendering1.pdf
Notes: dvr.pdf
vistrails: VolumeRenderingVistrails.zip
References: Optical Models for Direct Volume Rendering
10/23: Midterm 1
10/28: Direct Volume Rendering
Lecturer: Claudio
Topics: Structured grid techniques: ray-casting, splatting, texture slicing, shear-warp
Slides: VolumeRendering2.pdf
Notes: same as previous class
vistrails: same as previous class
References:
Display of Surfaces from Volume Data - Ray casting paper
Interactive Volume Rendering - Splatting paper, paper requires ACM digital library access
Accelerated volume rendering and tomographic reconstruction using texture mapping hardware - Texture slicing paper, requires ACM digital library access
Fast Volume Rendering Using a Shear-Warp Factorization of the Viewing Transformation - Shear-warp paper
10/30: Invited Lecture by Professor Joao Comba
Title: Edge Groups: An Approach to Understanding the Mesh Quality of Marching Methods
Abstract: Marching Cubes is the most popular isosurface extraction algorithm due to its simplicity, efficiency and robustness. It has been widely studied, improved, and extended. While much early work was concerned with efficiency and correctness issues, lately there has been a push to improve the quality of Marching Cubes meshes so that they can be used in computational codes. In this work we present a new classification of MC cases that we call Edge Groups, which helps elucidate the issues that impact the triangle quality of the meshes that the method generates. This formulation allows a more systematic way to bound the triangle quality, and is general enough to extend to other polyhedral cell shapes used in other polygonization algorithms. Using this analysis, we also discuss ways to improve the quality of the resulting triangle mesh, including some that require only minor modifications of the original algorithm.
This is joint work with Carlos A. Dietrich, Carlos E. Scheidegger, Luciana P. Nedel and Claudio T. Silva, and was presented last week at IEEE Visualization 2008.
Slides: pdf file
11/4: Direct Volume Rendering
Lecturer: Jens Kruger
Slides: unstructured_grid_rendering.pdf
References:
A Survey of GPU-Based Volume Rendering of Unstructured Grid
Hardware-Assisted Visibility Sorting for Unstructured Volume Rendering (This technique is implemented in VTK: http://www.vtk.org/doc/nightly/html/classvtkHAVSVolumeMapper.html)
ZSWEEP: An Efficient and Exact Projection Algorithm for Unstructured Volume Rendering (This technique is implemented in VTK: http://www.vtk.org/doc/nightly/html/classvtkUnstructuredGridVolumeZSweepMapper.html)
11/6: Direct Volume Rendering
Lecturer: Claudio
Topics: Transfer function specification
11/11: Direct Volume Rendering
Lecturer: Claudio
Topics: Transfer function specification
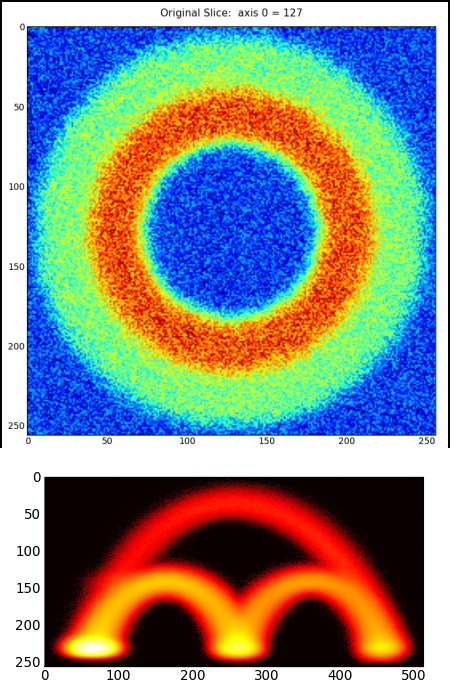
Additional Question:
The above image is the sphere data and joint histogram discussed in class. Which material boundary is highlighted by the small arc on the right-side of the histogram? The colors in the original dataset can be interpreted as:
0 = Blue
1 = Green
2 = Red
11/13: Tensor Visualization
Lecturer: Claudio
Topics: DT/MRI intro, glyphs, colormapping, volume rendering
11/15: 3D Vector Vis and Topology
Lecturer: Claudio
Topics: 3D techniques, critical points
11/18: Information Visualization
Lecturer: Claudio
Topics: Parallel coordinates; Graph visualization
11/20: Information Visualization
Lecturer: Claudio
Topics: Trees and Graphs; InfoVis Examples
11/25: TBD
11/27: Thanksgiving
12/2: Aesthetic Issues in Vis
Lecturer: Claudio
Topics: Tufte principles
12/4: Aesthetic Issues in Vis
Lecturer: Claudio
Topics: NPR and Illustrative techniques for Vis