User:Tohline/Appendix/Ramblings/PPTori
Stability Analyses of PP Tori

|
|---|
| | Tiled Menu | Tables of Content | Banner Video | Tohline Home Page | |
As has been summarized in an accompanying chapter — also see our related detailed notes — we have been trying to understand why unstable nonaxisymmetric eigenvectors have the shapes that they do in rotating toroidal configurations. For any azimuthal mode, <math>~m</math>, we are referring both to the radial dependence of the distortion amplitude, <math>~f_m(\varpi)</math>, and the radial dependence of the phase function, <math>~\phi_m(\varpi)</math> — the latter is what the Imamura and Hadley collaboration refer to as a "constant phase locus." Some old videos showing the development over time of various self-gravitating "constant phase loci" can be found here; these videos supplement the published work of Woodward, Tohline & Hachisu (1994).
Here, we focus specifically on instabilities that arise in so-called (non-self-gravitating) Papaloizou-Pringle tori and will draw heavily from two publications: (1) Papaloizou & Pringle (1987), MNRAS, 225, 267 — The dynamical stability of differentially rotating discs. III. — hereafter, PPIII — and (2) Blaes (1985), MNRAS, 216, 553 — Oscillations of slender tori.
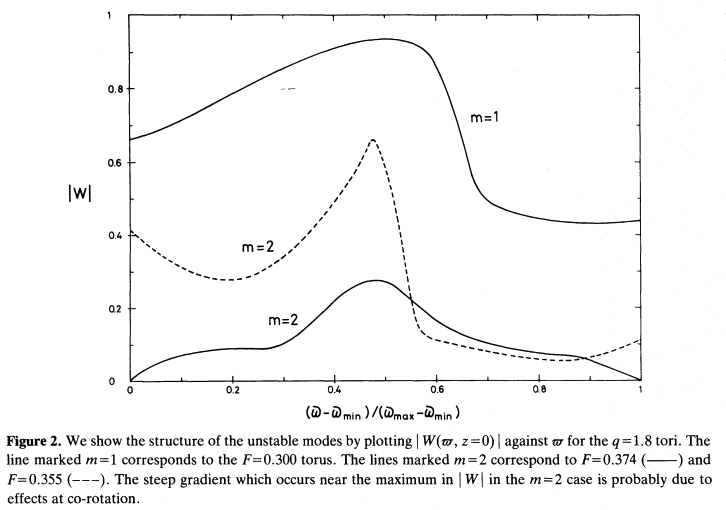
PP III
|
Figure 2 extracted without modification from p. 274 of J. C. B. Papaloizou & J. E. Pringle (1987)
"The Dynamical Stability of Differentially Rotating Discs. III"
MNRAS, vol. 225, pp. 267-283 © The Royal Astronomical Society |
Blaes85
His Notation
Blaes (1985) adopts a polytropic equation of state,
<math>~\frac{\rho}{\rho_c} = \Theta_H^n \, ,</math>
which gives rise to (slim tori) equilibrium structures for which (see his equation 1.3),
|
<math>~\Theta_H</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~1 - \frac{1}{\beta^2}\biggl[x^2 + x^3(3\cos\theta - \cos^3\theta) + \mathcal{O}(x^4) \biggr] \, ,</math> |
where, the (constant) model parameter,
<math>\beta \equiv \frac{(2n)^{1/2}}{\mathcal{M}_0} \, ,</math>
and <math>~\mathcal{M}_0</math> is the Mach number of the rotational velocity at the torus center. Blaes then adopts a related parameter that is constant on isobaric surfaces, namely,
<math>\eta^2 \equiv 1 - \Theta_H \, ,</math>
which is unity at the surface of the torus and which goes to zero at the cross-sectional center of the torus. Notice that <math>~\eta</math> tracks the "radial" coordinate that measures the distance from the center of the torus; in particular, keeping only the leading-order term in <math>~x</math>, there is a simple linear relationship between <math>~\eta</math> and <math>~x</math>, namely,
|
<math>~\eta</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~[1 - \Theta_H]^{1/2} \approx \frac{x}{\beta} \, .</math> |
Cubic Equation Solution
For later use, let's invert the cubic relation to obtain a more broadly applicable <math>~x(\eta)</math> function. Because we are only interested in radial profiles in the equatorial plane — that is, only for the values of <math>~\theta = 0</math> or <math>~\theta=\pi</math> — the relation to be inverted is,
|
<math>~x^2 \pm 2 x^3</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~(\beta\eta)^2</math> |
|
<math>~\Rightarrow ~~~~ x^3 \pm \tfrac{1}{2}x^2 \mp \tfrac{1}{2}(\beta\eta)^2</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~0 \, .</math> |
| Table 1: Example Parameter Values determined by iterative solution for <math>~\beta = \tfrac{1}{10}</math> | |||||
| <math>~\eta</math> | <math>~\Gamma^2 = 54\beta^2\eta^2</math> | Inner solution <math>~(\theta = 0)</math> [Superior sign in cubic eq.] | Outer solution <math>~(\theta = \pi)</math> [Inferior sign in cubic eq.] | ||
| <math>^\dagger\biggl(\frac{x_\mathrm{root}}{\beta}\biggr)</math> | <math>~6(S + T)</math> | <math>^\dagger\biggl(\frac{x_\mathrm{root}}{\beta}\biggr)</math> | <math>~6(S + T)</math> | ||
| 0.25 | 0.03375 | 0.244112 | 1.14647 | 0.256675 | -0.84600 |
| 1.0 | 0.54 | 0.91909 | 1.55145 | 1.1378 | -0.31732 |
|
†Here, <math>~x_\mathrm{root}</math> has been determined via a brute-force, iterative technique. |
|||||
Following Wolfram's discussion of the cubic formula, we should view this expression as a specific case of the general formula,
<math>~x^3 + a_2x^2 + a_1x + a_0 = 0 \, ,</math>
in which case, as is detailed in equations (54) - (56) of Wolfram's discussion of the cubic formula, the three roots of any cubic equation are:
|
<math>~x_1</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ -\frac{1}{3}a_2 + (S + T) \, , </math> |
|
<math>~x_2</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ -\frac{1}{3}a_2 - \frac{1}{2} (S + T) + \frac{1}{2} \it{i} \sqrt{3} (S-T)\, , </math> |
|
<math>~x_3</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ -\frac{1}{3}a_2 - \frac{1}{2} (S + T) - \frac{1}{2} \it{i} \sqrt{3} (S-T)\, , </math> |
where,
|
<math>~S</math> |
<math>~\equiv</math> |
<math>~[R + \sqrt{D}]^{1/3} \, ,</math> |
|
<math>~T</math> |
<math>~\equiv</math> |
<math>~[R - \sqrt{D}]^{1/3} \, ,</math> |
|
<math>~D</math> |
<math>~\equiv</math> |
<math>~Q^3 + R^2 \, ,</math> |
|
<math>~Q</math> |
<math>~\equiv</math> |
<math>~\frac{3a_1 - a_2^2}{3^2} \, ,</math> |
|
<math>~R</math> |
<math>~\equiv</math> |
<math>~\frac{3^2a_2 a_1 - 3^3a_0 - 2a_2^3}{2\cdot 3^3} \, . </math> |
Material that appears after this point in our presentation is under development and therefore
may contain incorrect mathematical equations and/or physical misinterpretations.
| Go Home |
Outer [inferior sign] Solution
Focusing, first, on the inferior sign convention, which corresponds to the "outer" solution <math>~(\theta = \pi)</math>, we see that the coefficients that lead to our specific cubic equation are:
|
<math>~a_2</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~- \tfrac{1}{2} \, ,</math> |
|
<math>~a_1</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~0 \, ,</math> |
|
<math>~a_0</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\tfrac{1}{2}(\beta\eta)^2 \, .</math> |
Applying Wolfram's definitions of the <math>~Q</math> and <math>~R</math> parameters to our particular problem gives,
|
<math>~Q</math> |
<math>~\equiv</math> |
<math>~\frac{3a_1 - a_2^2}{3^2} = -\biggl(\frac{a_2}{3}\biggr)^2 = - \frac{1}{2^2\cdot 3^2} \, ;</math> |
|
<math>~R</math> |
<math>~\equiv</math> |
<math>~\frac{3^2a_2 a_1 - 3^3a_0 - 2a_2^3}{2\cdot 3^3} = \frac{1}{2\cdot 3^3} \biggl[ -\frac{ 3^3}{2}(\beta\eta)^2 + \frac{1}{2^2}\biggr] </math> |
|
|
<math>~\equiv</math> |
<math>~\frac{1}{2^3\cdot 3^3} \biggl[ 1 - 2\cdot 3^3(\beta\eta)^2\biggr] \, . </math> |
Defining the parameter,
|
<math>~\Gamma^2</math> |
<math>~\equiv</math> |
<math>~ 2\cdot 3^3(\beta\eta)^2 \, ,</math> |
we therefore have,
|
<math>~(2\cdot 3)^6 D</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~( 1 - \Gamma^2 )^2-1 \, ,</math> |
|
<math>~(2\cdot 3)^3S^3</math> |
<math>~\equiv</math> |
<math>~(2\cdot 3)^3 R + \sqrt{(2\cdot 3)^6D} </math> |
|
|
<math>~\equiv</math> |
<math>~(1-\Gamma^2) + \sqrt{( 1 - \Gamma^2 )^2-1}</math> |
|
|
<math>~\equiv</math> |
<math>~(1-\Gamma^2) + i\sqrt{1-( 1 - \Gamma^2 )^2} \, ;</math> |
|
<math>~(2\cdot 3)^3T^3</math> |
<math>~\equiv</math> |
<math>~(1-\Gamma^2) - i\sqrt{1-( 1 - \Gamma^2 )^2} \, .</math> |
|
ASIDE: The cube root of an imaginary number …
where,
and,
Now, according to this online resource, the three roots <math>~(j=0,1,2)</math> of <math>~\ell^3</math> are,
which, for our specific problem gives,
where the subscript on <math>~\theta</math> refers to the <math>~\pm</math> in our original expression for <math>~\ell</math>.
|
In our particular case, after associating <math>~A \leftrightarrow (1-\Gamma^2)</math>, we can write,
|
<math>~ 2\cdot 3(S + T) </math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \biggl[(1-\Gamma^2) + i\sqrt{1-( 1 - \Gamma^2 )^2} \biggr]^{1/3} + \biggl[(1-\Gamma^2) - i\sqrt{1-( 1 - \Gamma^2 )^2} \biggr]^{1/3} </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ e^{i\theta_+/3} \cdot e^{i(2j\pi/3)} + e^{i\theta_-/3} \cdot e^{i(2j\pi/3)} </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~e^{i(2j\pi/3)} \biggl\{ e^{i[\cos^{-1}(1-\Gamma^2)]/3} + e^{-i[\cos^{-1}(1-\Gamma^2)]/3} \biggr\} </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~e^{i(2j\pi/3)} \biggl\{\cos\biggl[ \tfrac{1}{3}\cos^{-1}(1-\Gamma^2)\biggr] + i\sin\biggl[ \tfrac{1}{3} \cos^{-1}(1-\Gamma^2)\biggr] </math> |
|
|
|
<math>~+ \cos\biggl[ \tfrac{1}{3} \cos^{-1}(1-\Gamma^2)\biggr] - i\sin\biggl[ \tfrac{1}{3} \cos^{-1}(1-\Gamma^2)\biggr] \biggr\} </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~2 e^{i(2j\pi/3)} \cdot \cos\biggl[ \tfrac{1}{3}\cos^{-1}(1-\Gamma^2)\biggr] \, .</math> |
Similarly, we can write,
|
<math>~ 2\cdot 3(S - T) </math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \biggl[(1-\Gamma^2) + i\sqrt{1-( 1 - \Gamma^2 )^2} \biggr]^{1/3} - \biggl[(1-\Gamma^2) - i\sqrt{1-( 1 - \Gamma^2 )^2} \biggr]^{1/3} </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ e^{i\theta_+/3} \cdot e^{i(2j\pi/3)} - e^{i\theta_-/3} \cdot e^{i(2j\pi/3)} </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~e^{i(2j\pi/3)} \biggl\{ e^{i[\cos^{-1}(1-\Gamma^2)]/3} - e^{-i[\cos^{-1}(1-\Gamma^2)]/3} \biggr\} </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~e^{i(2j\pi/3)} \biggl\{\cos\biggl[ \tfrac{1}{3}\cos^{-1}(1-\Gamma^2)\biggr] + i\sin\biggl[ \tfrac{1}{3} \cos^{-1}(1-\Gamma^2)\biggr] </math> |
|
|
|
<math>~- \cos\biggl[ \tfrac{1}{3} \cos^{-1}(1-\Gamma^2)\biggr] + i\sin\biggl[ \tfrac{1}{3} \cos^{-1}(1-\Gamma^2)\biggr] \biggr\} </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~2i e^{i(2j\pi/3)} \cdot \sin\biggl[ \tfrac{1}{3}\cos^{-1}(1-\Gamma^2)\biggr] \, . </math> |
Focusing specifically on the "j=0" root, and setting <math>~a_2 = -\tfrac{1}{2}</math>, we therefore have,
|
<math>~6x_1-1</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ 6(S + T) </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~2 \cos\biggl[ \tfrac{1}{3}\cos^{-1}(1-\Gamma^2)\biggr] \, ;</math> |
|
<math>~6x_2-1</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ - \frac{1}{2} \biggl\{ 2 \cos\biggl[ \tfrac{1}{3}\cos^{-1}(1-\Gamma^2)\biggr] - i\sqrt{3} \cdot 2i \sin\biggl[ \tfrac{1}{3}\cos^{-1}(1-\Gamma^2)\biggr] \biggr\} </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ -2\biggl\{ \frac{1}{2}\cdot \cos\biggl[ \tfrac{1}{3}\cos^{-1}(1-\Gamma^2)\biggr] +\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \cdot \sin\biggl[ \tfrac{1}{3}\cos^{-1}(1-\Gamma^2)\biggr] \biggr\} </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ 2\biggl\{ \cos\biggl[ \tfrac{1}{3}\cos^{-1}(1-\Gamma^2) + \frac{2\pi}{3}\biggr] \biggr\} \, ; </math> |
|
<math>~6x_3-1</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ - \frac{1}{2} \biggl\{ 2 \cos\biggl[ \tfrac{1}{3}\cos^{-1}(1-\Gamma^2)\biggr] + i\sqrt{3} \cdot 2i \sin\biggl[ \tfrac{1}{3}\cos^{-1}(1-\Gamma^2)\biggr] \biggr\} </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ -2\biggl\{ \frac{1}{2}\cdot \cos\biggl[ \tfrac{1}{3}\cos^{-1}(1-\Gamma^2)\biggr] -\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \cdot \sin\biggl[ \tfrac{1}{3}\cos^{-1}(1-\Gamma^2)\biggr] \biggr\} </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ 2\biggl\{ \cos\biggl[ \tfrac{1}{3}\cos^{-1}(1-\Gamma^2) - \frac{2\pi}{3}\biggr] \biggr\} \, . </math> |
| Table 1: Analytically Evaluated Roots determined for <math>~\beta = \tfrac{1}{10}</math> | |||||||
| <math>~\eta</math> | <math>~\Gamma^2 = 54\beta^2\eta^2</math> | Inner solution <math>~(\theta = 0)</math> [Superior sign in cubic eq.] | Outer solution <math>~(\theta = \pi)</math> [Inferior sign in cubic eq.] | ||||
| <math>~x_1/\beta</math> | <math>~x_2/\beta</math> | <math>~x_3/\beta</math> | <math>~x_1/\beta</math> | <math>~x_2/\beta</math> | <math>~x_3/\beta</math> | ||
| 0.25 | 0.03375 | --- | --- | --- | 4.98744 | -0.24411 | 0.25667 |
| 1.0 | 0.54 | --- | --- | --- | 4.78128 | -0.91909 | 1.1378 |
| CONFIRMATION: In all cases, <math>~x^2 + 2x^3 = (\beta\eta)^2</math> | CONFIRMATION: In all cases, <math>~x^2 - 2x^3 = (\beta\eta)^2</math> | ||||||
Inner [superior sign] Solution
Next, examing the superior sign convention, which corresponds to the "inner" solution <math>~(\theta = 0)</math>, we see that the coefficients that lead to our specific cubic equation are:
|
<math>~a_2</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\tfrac{1}{2} \, ,</math> |
|
<math>~a_1</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~0 \, ,</math> |
|
<math>~a_0</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~- \tfrac{1}{2}(\beta\eta)^2 \, .</math> |
Following the same set of steps that were followed in determining the "outer" solution, here we find: <math>~Q</math> remains the same; <math>~R</math> has the same magnitude, but changes sign; and, hence, <math>~D</math> remains the same. We therefore have,
|
<math>~(2\cdot 3)^3S^3</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~- (1-\Gamma^2) + i\sqrt{1-( 1 - \Gamma^2 )^2} \, ;</math> |
|
<math>~(2\cdot 3)^3T^3</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~- (1-\Gamma^2) - i\sqrt{1-( 1 - \Gamma^2 )^2} \, .</math> |
|
<math>~6x_1+1</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~2 \cos\biggl[ \tfrac{1}{3}\cos^{-1}(1+\Gamma^2)\biggr] \, ;</math> |
|
<math>~6x_2+1</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ 2\biggl\{ \cos\biggl[ \tfrac{1}{3}\cos^{-1}(1+\Gamma^2) + \frac{2\pi}{3}\biggr] \biggr\} \, ; </math> |
|
<math>~6x_3+1</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ 2\biggl\{ \cos\biggl[ \tfrac{1}{3}\cos^{-1}(1+\Gamma^2) - \frac{2\pi}{3}\biggr] \biggr\} \, . </math> |
Analytically Prescribed Eigenvector
From my initial focused reading of the analysis presented by Blaes (1985), I conclude that, in the infinitely slender torus case, unstable modes in PP tori exhibit eigenvectors of the form,
|
<math>~\frac{\delta W}{W_0} \equiv \biggl[ \frac{W(\eta,\theta)}{C} - 1 \biggr]e^{im\Omega_p t}e^{-y_2 (\Omega_0 t)} </math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\biggl\{ f_m(\eta,\theta)e^{-i[m\phi_m(\varpi) + k\theta]} \biggr\} \, ,</math> |
where we have written the perturbation amplitude in a manner that conforms with the notation that we have used in Figure 1 of a related, but more general discussion. As is summarized in §1.3 of Blaes (1985), for "thick" (but, actually, still quite thin) tori, "exactly one exponentially growing mode exists for each value of the azimuthal wavenumber <math>~m</math>," and its complex amplitude takes the following form (see his equation 1.10):
|
<math>~f_m(\eta,\theta)</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math> ~\beta^2 m^2 \biggl[ 2\eta^2 \cos^2\theta - \frac{3\eta^2}{4(n+1)} - \frac{(4n+1)}{4(n+1)^2} \pm 4i\biggl(\frac{3}{2n+2}\biggr)^{1/2} \eta\cos\theta\biggr] + \mathcal{O}(\beta^3) \, . </math> |
We should therefore find that the amplitude (modulus) of the enthalpy perturbation is,
|
<math>~\biggl|\frac{\delta W}{W_0} \biggr|</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\sqrt{[\mathrm{Re}(f_m)]^2+ [\mathrm{Im}(f_m)]^2} \, ;</math> |
and the associated phase function should be,
|
<math>~m\phi_m + k\theta</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\tan^{-1} \biggl\{ \frac{-\mathrm{Re}(f_m)}{\mathrm{Im}(f_m)} \biggr\}</math> |
Now, keeping in mind that, for the time being, we are only interested in examining the shape of the unstable eigenvector in the equatorial plane of the torus, we can set,
<math>~\cos\theta ~~ \rightarrow ~~ \pm 1 \, .</math>
Hence, we have,
|
<math>~\frac{1}{\beta^4 m^4}\biggl|\frac{\delta W}{W_0} \biggr|^2</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\biggl[2\eta^2 - \frac{3\eta^2}{4(n+1)} - \frac{(4n+1)}{4(n+1)^2}\biggr]^2 + 16\biggl[\biggl(\frac{3}{2n+2}\biggr)^{1/2} \eta \biggr]^2 </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\frac{1}{[2^2(n+1)^2]^2}\biggl[2^3(n+1)^2\eta^2 - 3(n+1)\eta^2 - (4n+1) \biggr]^2 + \frac{2^3 \cdot 3\eta^2}{(n+1)} </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\frac{1}{[2^2(n+1)^2]^2}\biggl[(4n+1) - (n+1)[2^3(n+1)-3]\eta^2 \biggr]^2 + \frac{2^3 \cdot 3\eta^2}{(n+1)} </math> |
|
<math>~\Rightarrow ~~~~ \biggl[\frac{2(n+1)}{\beta m} \biggr]^4 \biggl|\frac{\delta W}{W_0} \biggr|^2</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\biggl[(4n+1) - (n+1)[2^3(n+1)-3]\eta^2 \biggr]^2 + 2^7 \cdot 3(n+1)^3\eta^2 \, . </math> |
Also,
|
<math>~m\phi_m</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\tan^{-1}\biggl\{ \frac{(4n+1) - (n+1)[2^3(n+1)-3]\eta^2 }{2^{7/2}\cdot 3^{1/2}(n+1)^{3/2}\eta} \biggr\}</math> |
over |
inner region of the torus; |
|
| while | |||||
|
<math>~m\phi_m</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\tan^{-1}\biggl\{ \frac{(4n+1) - (n+1)[2^3(n+1)-3]\eta^2 }{2^{7/2}\cdot 3^{1/2}(n+1)^{3/2}\eta} \biggr\} - k\pi</math> |
over |
outer region of torus. |
|
See Also
- Imamura & Hadley collaboration:
- Paper I: K. Hadley & J. N. Imamura (2011, Astrophysics and Space Science, 334, 1-26), "Nonaxisymmetric instabilities in self-gravitating disks. I. Toroids" — In this paper, Hadley & Imamura perform linear stability analyses on fully self-gravitating toroids; that is, there is no central point-like stellar object and, hence, <math>~M_*/M_d = 0.0</math>.
- Paper II: K. Z. Hadley, P. Fernandez, J. N. Imamura, E. Keever, R. Tumblin, & W. Dumas (2014, Astrophysics and Space Science, 353, 191-222), "Nonaxisymmetric instabilities in self-gravitating disks. II. Linear and quasi-linear analyses" — In this paper, the Imamura & Hadley collaboration performs "an extensive study of nonaxisymmetric global instabilities in thick, self-gravitating star-disk systems creating a large catalog of star/disk systems … for star masses of <math>~0.0 \le M_*/M_d \le 10^3</math> and inner to outer edge aspect ratios of <math>~0.1 < r_-/r_+ < 0.75</math>."
- Paper III: K. Z. Hadley, W. Dumas, J. N. Imamura, E. Keever, & R. Tumblin (2015, Astrophysics and Space Science, 359, article id. 10, 23 pp.), "Nonaxisymmetric instabilities in self-gravitating disks. III. Angular momentum transport" — In this paper, the Imamura & Hadley collaboration carries out nonlinear simulations of nonaxisymmetric instabilities found in self-gravitating star/disk systems and compares these results with the linear and quasi-linear modeling results presented in Papers I and II.

|
|---|
|
© 2014 - 2021 by Joel E. Tohline |