Difference between revisions of "User:Tohline/ThreeDimensionalConfigurations/ChallengesPt4"
(Created page with '__FORCETOC__<!-- will force the creation of a Table of Contents --> <!-- __NOTOC__ will force TOC off --> =Challenges Constructing Ellipsoidal-Like Configurations (Pt. 4)= This…') |
|||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
====Summary==== | |||
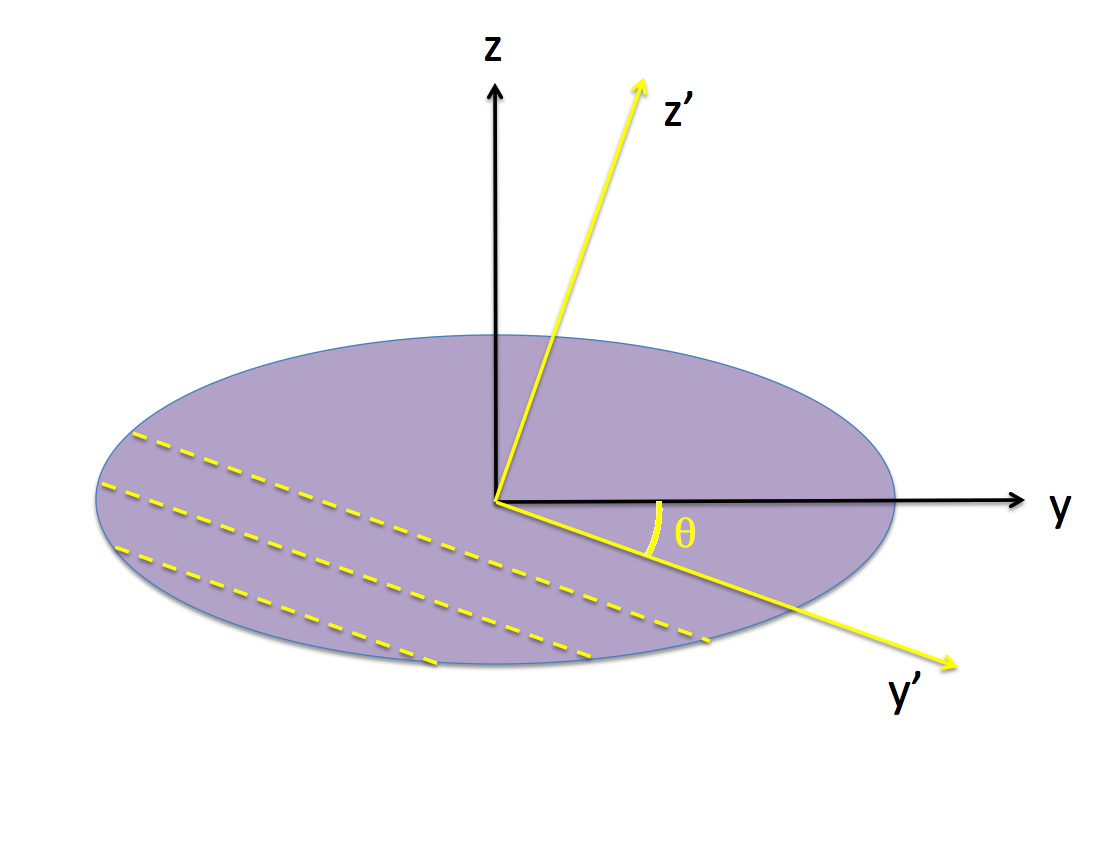
In a [[User:Tohline/ThreeDimensionalConfigurations/RiemannTypeI#Try_Again|separate discussion]], we have shown that, as viewed from a frame that "tumbles" with the (purple) body of a Type 1 Riemann ellipsoid, each Lagrangian fluid element moves along an elliptical path in a plane that is tipped by an angle <math>~\theta</math> about the x-axis of the body. As viewed from the (primed) coordinates associated with this tipped plane, by definition, z' = constant and dz'/dt = 0, and the planar orbit is defined by the expression for an, | |||
<table border="0" cellpadding="5" align="center"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td align="center" colspan="3"><font color="maroon">'''Off-Center Ellipse'''</font></td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td align="right"> | |||
<math>~1</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="center"> | |||
<math>~=</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="left"> | |||
<math>~\biggl[\frac{x'}{x_\mathrm{max}} \biggr]^2 + \biggl[\frac{y' - y_c(z')}{y_\mathrm{max}} \biggr]^2 \, .</math> | |||
</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
<table border="0" cellpadding="10" align="right" width="30%"><tr><td align="center"> | |||
<table border="1" align="center" cellpadding="8"> | |||
<tr><td align="center"> | |||
''Tipped Orbit Frame'' (yellow, primed) <br /> | |||
</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td align="center">[[File:TippedAxes03.png|350px|Tipped Orbital Planes]]</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr><td align="center"> | |||
Given that b/a = 1.25 and c/a = 0.4703 for our chosen [[User:Tohline/ThreeDimensionalConfigurations/ChallengesPt2#Example_Equilibrium_Model|Example Type I Ellipsoid]], we find that, <math>~\theta = - 1.18122 ~\mathrm{rad} = -67.68^\circ</math>. | |||
</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
</td></tr></table> | |||
Notice that the offset, <math>~y_c</math>, is a function of the tipped plane's vertical coordinate, <math>~z'</math>. As a function of time, the x'-y' coordinates and associated velocity components of each Lagrangian fluid element are given by the expressions, | |||
<table border="0" cellpadding="5" align="center"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td align="right"> | |||
<math>~x'</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="center"> | |||
<math>~=</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="left"> | |||
<math>~x_\mathrm{max}\cos(\dot\varphi t)</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="center"> and, | |||
<td align="right"> | |||
<math>~y' - y_c</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="center"> | |||
<math>~=</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="left"> | |||
<math>~y_\mathrm{max}\sin(\dot\varphi t) \, ,</math> | |||
</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td align="right"> | |||
<math>~\dot{x}'</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="center"> | |||
<math>~=</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="left"> | |||
<math>~- x_\mathrm{max}~ \dot\varphi \cdot \sin(\dot\varphi t) = (y_c - y') \biggl[ \frac{x_\mathrm{max}}{y_\mathrm{max}} \biggr] \dot\varphi </math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="center"> and, | |||
<td align="right"> | |||
<math>~\dot{y}' </math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="center"> | |||
<math>~=</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="left"> | |||
<math>~y_\mathrm{max}~\dot\varphi \cdot \cos(\dot\varphi t) = x' \biggl[ \frac{y_\mathrm{max}}{x_\mathrm{max}}\biggr] \dot\varphi \, .</math> | |||
</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
We have determined that (numerical value given for our chosen example Type I ellipsoid), | |||
<table border="0" cellpadding="5" align="center"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td align="right"> | |||
<math>~\tan\theta</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="center"> | |||
<math>~=</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="left"> | |||
<math>~ | |||
- \frac{b^2 \beta \Omega_2}{c^2 \gamma \Omega_3} | |||
= | |||
-2.43573\, , | |||
</math> | |||
</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
where, <math>~\beta</math> and <math>~\gamma</math> are as [[User:Tohline/ThreeDimensionalConfigurations/ChallengesPt3#betagamma|defined in an accompanying discussion]]. Also, | |||
<font color="red"><b>START HERE</b></font> | |||
<table border="0" cellpadding="5" align="center"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td align="right"> | |||
<math>~\biggl[\frac{x_\mathrm{max}}{y_\mathrm{max}} \biggr]^2</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="center"> | |||
<math>~=</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="left"> | |||
<math>~ | |||
\frac{a^2}{b^2 c^2} (c^2\cos^2\theta + b^2\sin^2\theta) | |||
= 1.05238 \, , | |||
</math> | |||
</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td align="right"> | |||
<math>~{\dot\varphi}^2 </math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="center"> | |||
<math>~=</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="left"> | |||
<math>~ | |||
\zeta_3^2\biggl[ \frac{b^2}{a^2 + b^2} \biggr]^2 | |||
\biggl[ \frac{x_\mathrm{max}}{y_\mathrm{max}} \biggr]^2 \biggl[1 + \tan^2\theta \biggr] | |||
= 1.68818\, , | |||
</math> | |||
</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td align="right"> | |||
<math>~y_c</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="center"> | |||
<math>~=</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="left"> | |||
<math>~+ \frac{z' b^2 \tan\theta}{c^2 \cos^2\theta + b^2\sin^2\theta} | |||
= | |||
+z' \tan\theta \biggl[\frac{y_\mathrm{max}}{x_\mathrm{max}} \biggr]^2 \frac{a^2}{c^2} | |||
= | |||
\biggl( \frac{z'}{ \cos\theta }\biggr)(-1.40038) | |||
\, .</math> | |||
</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
Note that this last expression has been obtained by making the substitutions, <math>~y_0 \rightarrow y_c</math> and <math>~z_0 \rightarrow -z'/\cos\theta</math>, in the [[User:Tohline/ThreeDimensionalConfigurations/ChallengesPt2#OffCenter|accompanying derivation's expression]] for <math>~y_0</math>. | |||
====Demonstration==== | |||
=See Also= | =See Also= | ||
Revision as of 16:43, 30 April 2021
Challenges Constructing Ellipsoidal-Like Configurations (Pt. 4)
This chapter extends the accompanying chapters titled, Construction Challenges (Pt. 1), (Pt. 2), and (Pt. 3). The focus here is on firming up our understanding of the relationships between various "tilted" Cartesian coordinate frames.

|
|---|
| | Tiled Menu | Tables of Content | Banner Video | Tohline Home Page | |
Various Coordinate Frames
Summary
In a separate discussion, we have shown that, as viewed from a frame that "tumbles" with the (purple) body of a Type 1 Riemann ellipsoid, each Lagrangian fluid element moves along an elliptical path in a plane that is tipped by an angle <math>~\theta</math> about the x-axis of the body. As viewed from the (primed) coordinates associated with this tipped plane, by definition, z' = constant and dz'/dt = 0, and the planar orbit is defined by the expression for an,
| Off-Center Ellipse | ||
|
<math>~1</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\biggl[\frac{x'}{x_\mathrm{max}} \biggr]^2 + \biggl[\frac{y' - y_c(z')}{y_\mathrm{max}} \biggr]^2 \, .</math> |
|
Notice that the offset, <math>~y_c</math>, is a function of the tipped plane's vertical coordinate, <math>~z'</math>. As a function of time, the x'-y' coordinates and associated velocity components of each Lagrangian fluid element are given by the expressions,
|
<math>~x'</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~x_\mathrm{max}\cos(\dot\varphi t)</math> |
and, |
<math>~y' - y_c</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~y_\mathrm{max}\sin(\dot\varphi t) \, ,</math> |
|
<math>~\dot{x}'</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~- x_\mathrm{max}~ \dot\varphi \cdot \sin(\dot\varphi t) = (y_c - y') \biggl[ \frac{x_\mathrm{max}}{y_\mathrm{max}} \biggr] \dot\varphi </math> |
and, |
<math>~\dot{y}' </math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~y_\mathrm{max}~\dot\varphi \cdot \cos(\dot\varphi t) = x' \biggl[ \frac{y_\mathrm{max}}{x_\mathrm{max}}\biggr] \dot\varphi \, .</math> |
We have determined that (numerical value given for our chosen example Type I ellipsoid),
|
<math>~\tan\theta</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ - \frac{b^2 \beta \Omega_2}{c^2 \gamma \Omega_3} = -2.43573\, , </math> |
where, <math>~\beta</math> and <math>~\gamma</math> are as defined in an accompanying discussion. Also,
START HERE
|
<math>~\biggl[\frac{x_\mathrm{max}}{y_\mathrm{max}} \biggr]^2</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \frac{a^2}{b^2 c^2} (c^2\cos^2\theta + b^2\sin^2\theta) = 1.05238 \, , </math> |
|
<math>~{\dot\varphi}^2 </math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \zeta_3^2\biggl[ \frac{b^2}{a^2 + b^2} \biggr]^2 \biggl[ \frac{x_\mathrm{max}}{y_\mathrm{max}} \biggr]^2 \biggl[1 + \tan^2\theta \biggr] = 1.68818\, , </math> |
|
<math>~y_c</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~+ \frac{z' b^2 \tan\theta}{c^2 \cos^2\theta + b^2\sin^2\theta} = +z' \tan\theta \biggl[\frac{y_\mathrm{max}}{x_\mathrm{max}} \biggr]^2 \frac{a^2}{c^2} = \biggl( \frac{z'}{ \cos\theta }\biggr)(-1.40038) \, .</math> |
Note that this last expression has been obtained by making the substitutions, <math>~y_0 \rightarrow y_c</math> and <math>~z_0 \rightarrow -z'/\cos\theta</math>, in the accompanying derivation's expression for <math>~y_0</math>.
Demonstration
See Also
- Riemann Type 1 Ellipsoids
- Construction Challenges (Pt. 1)
- Construction Challenges (Pt. 2)
- Construction Challenges (Pt. 3)
- Construction Challenges (Pt. 4)
- Related discussions of models viewed from a rotating reference frame:
- PGE
- NOTE to Eric Hirschmann & David Neilsen... I have moved the earlier contents of this page to a new Wiki location called Compressible Riemann Ellipsoids.

|
|---|
|
© 2014 - 2021 by Joel E. Tohline |