Difference between revisions of "User:Tohline/Appendix/CGH/Overview"
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
</td></tr></table> | </td></tr></table> | ||
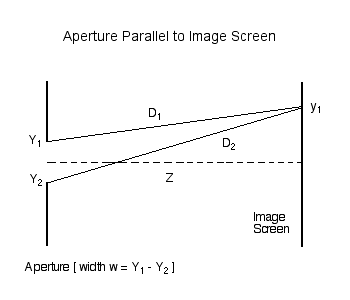
As has been detailed in an [[User:Tohline/Appendix/CGH/ParallelApertures#One-Dimensional_Aperture|accompanying discussion]], we | As has been detailed in an [[User:Tohline/Appendix/CGH/ParallelApertures#One-Dimensional_Aperture|accompanying discussion]], we examine, first, the amplitude (and phase) of light which, after passing through an aperture of width <math>~w = (Y_1 - Y_2) = 2c</math>, is incident on an image screen that is parallel to, and located a distance <math>~Z</math> from, the aperture. The amplitude at any location, <math>~y_1</math>, along the image screen is given by the expression, | ||
<div align="center"> | <div align="center"> | ||
<table border="0" cellpadding="5" align="center"> | <table border="0" cellpadding="5" align="center"> | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td align="right"> | <td align="right"> | ||
<math>~A( | <math>~A(y_1)</math> | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
<td align="center"> | <td align="center"> | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
<td align="left"> | <td align="left"> | ||
<math>~\sum_j | <math>~\sum_j | ||
\beta_j \biggl[ \cos\biggl(\frac{2\pi D_j}{\lambda} + \phi_j \biggr) + i \sin\biggl(\frac{2\pi D_j}{\lambda} + \phi_j \biggr) \biggr] | |||
\, , | \, , | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
where, <math>~ | where, <math>~\beta_j = \beta(Y_j)</math> is the specified brightness at each "j" point along the illuminated aperture, | ||
<div align="center" id="Distance"> | <div align="center" id="Distance"> | ||
<table border="0" cellpadding="5" align="center"> | <table border="0" cellpadding="5" align="center"> | ||
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Notice that, in the definition of <math>~D_j</math>, the expression inside the square brackets involves a term that depends quadratically on the dimensionless length scale, <math>~Y_j/L</math>, as well as a term that depends linearly on this ratio. As discussed below, our expression for the amplitude simplifies nicely in situations where the quadratic term can be ignored. Via a related simplification, we also will find that the various natural lengths of this problem | |||
The green solid curves in [[User:Tohline/Appendix/CGH/ParallelApertures#Figure2|Figures 2 & 3 of our accompanying, more detailed discussion]] display — for a fixed set of values of the parameter-pair, <math>~(\lambda, w)</math> — how the amplitude of the incident light, <math>~(A\cdot A^*)^{1 / 2}</math>, varies across an image screen that is placed at two different distances from the aperture. | |||
Notice that, in the definition of <math>~D_j</math>, the expression inside the square brackets involves a term that depends quadratically on the dimensionless length scale, <math>~Y_j/L</math>, as well as a term that depends linearly on this ratio. As [[#Simplifications|discussed below]], our expression for the amplitude simplifies nicely in situations where the quadratic term can be ignored. (The red dotted curves in [[User:Tohline/Appendix/CGH/ParallelApertures#Figure2|Figures 2 & 3 of our accompanying discussion]] illustrate how the image-screen diffraction pattern is altered as a result of this simplification.) Via a related simplification, we also will find that the various natural lengths of this problem can be related to one another via the expression, | |||
<div align="center"> | <div align="center"> | ||
<table border="0" cellpadding="5" align="center"> | <table border="0" cellpadding="5" align="center"> | ||
| Line 94: | Line 97: | ||
CAUTION: Be sure that the "L" in these various expressions is, indeed, always the same quantity. | CAUTION: Be sure that the "L" in these various expressions is, indeed, always the same quantity. | ||
===Simplifications=== | |||
If we assume that everywhere along the aperture the phase <math>~\phi_j = 0</math>; and if we assume that, for all <math>~j</math>, | |||
<div align="center"> | |||
<math>~\biggl| \frac{Y_j}{L}\biggr| \ll 1</math> | |||
</div> | |||
we can drop the quadratic term in favor of the linear one in the above expression for <math>~D_j</math> and [[User:Tohline/Appendix/CGH/ParallelApertures#Simplify|deduce that]], | |||
<div align="center"> | |||
<table border="0" cellpadding="5" align="center"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td align="right"> | |||
<math>~A(y_1)</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="center"> | |||
<math>~\approx</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="left"> | |||
<math>~e^{i2\pi L/\lambda} \sum_j | |||
\beta_j \biggl[ \cos\biggl(\frac{2\pi y_1 Y_j}{\lambda L} \biggr) - i \sin\biggl(\frac{2\pi y_1 Y_j}{\lambda L} \biggr) \biggr] | |||
\, . | |||
</math> | |||
</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
</div> | |||
=See Also= | =See Also= | ||
Revision as of 22:19, 28 December 2017
CGH: Philosophical Overview

|
|---|
| | Tiled Menu | Tables of Content | Banner Video | Tohline Home Page | |
Slit Diffraction
Single Aperture
|
As has been detailed in an accompanying discussion, we examine, first, the amplitude (and phase) of light which, after passing through an aperture of width <math>~w = (Y_1 - Y_2) = 2c</math>, is incident on an image screen that is parallel to, and located a distance <math>~Z</math> from, the aperture. The amplitude at any location, <math>~y_1</math>, along the image screen is given by the expression,
|
<math>~A(y_1)</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\sum_j \beta_j \biggl[ \cos\biggl(\frac{2\pi D_j}{\lambda} + \phi_j \biggr) + i \sin\biggl(\frac{2\pi D_j}{\lambda} + \phi_j \biggr) \biggr] \, , </math> |
where, <math>~\beta_j = \beta(Y_j)</math> is the specified brightness at each "j" point along the illuminated aperture,
|
<math>~D_j</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ L \biggl[1 - \frac{2y_1 Y_j}{L^2} + \frac{Y_j^2}{L^2} \biggr]^{1 / 2} \, , </math> |
and,
|
<math>~L</math> |
<math>~\equiv</math> |
<math>~ [Z^2 + y_1^2 ]^{1 / 2} \, . </math> |
The green solid curves in Figures 2 & 3 of our accompanying, more detailed discussion display — for a fixed set of values of the parameter-pair, <math>~(\lambda, w)</math> — how the amplitude of the incident light, <math>~(A\cdot A^*)^{1 / 2}</math>, varies across an image screen that is placed at two different distances from the aperture.
Notice that, in the definition of <math>~D_j</math>, the expression inside the square brackets involves a term that depends quadratically on the dimensionless length scale, <math>~Y_j/L</math>, as well as a term that depends linearly on this ratio. As discussed below, our expression for the amplitude simplifies nicely in situations where the quadratic term can be ignored. (The red dotted curves in Figures 2 & 3 of our accompanying discussion illustrate how the image-screen diffraction pattern is altered as a result of this simplification.) Via a related simplification, we also will find that the various natural lengths of this problem can be related to one another via the expression,
|
<math>~y_1\biggr|_{1^\mathrm{st} \mathrm{fringe}} = \frac{L \Delta y_1}{c}</math> |
<math>~\approx</math> |
<math>~\frac{\lambda Z}{2c} \, .</math> |
CAUTION: Be sure that the "L" in these various expressions is, indeed, always the same quantity.
Simplifications
If we assume that everywhere along the aperture the phase <math>~\phi_j = 0</math>; and if we assume that, for all <math>~j</math>,
<math>~\biggl| \frac{Y_j}{L}\biggr| \ll 1</math>
we can drop the quadratic term in favor of the linear one in the above expression for <math>~D_j</math> and deduce that,
|
<math>~A(y_1)</math> |
<math>~\approx</math> |
<math>~e^{i2\pi L/\lambda} \sum_j \beta_j \biggl[ \cos\biggl(\frac{2\pi y_1 Y_j}{\lambda L} \biggr) - i \sin\biggl(\frac{2\pi y_1 Y_j}{\lambda L} \biggr) \biggr] \, . </math> |
See Also
- Tohline, J. E., (2008) Computing in Science & Engineering, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 84-85 — Where is My Digital Holographic Display? [ PDF ]
- Diffraction (Wikipedia)
- Various Google hits:
- Single Slit Diffraction (University of Tennessee, Knoxville)
- Diffraction from a Single Slit; Young's Experiment with Finite Slits (University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia)
- Single Slit Diffraction Pattern of Light (University of British Columbia, Canada)
- Fraunhofer Single Slit (Georgia State University)

|
|---|
|
© 2014 - 2021 by Joel E. Tohline |