Difference between revisions of "User:Tohline/Apps/PapaloizouPringleTori"
(→Solution: Add text to allow simpler comparison of solutions) |
(→Solution: More clarification of torus structure) |
||
| Line 83: | Line 83: | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
The algebraic relation defining the equilibrium structure then becomes, | The algebraic relation defining the equilibrium structure then becomes, | ||
| Line 97: | Line 96: | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
===Pressure Maximum=== | |||
It is instructive to examine at what location inside the torus the enthalpy (and density and gas pressure) assumes its maximum value. At any radial location, <math>\chi_i</math>, <math>H</math> has a vertical maximum where <math>\partial H/\partial\zeta = 0.</math> That is, the maximum occurs where, | |||
<div align="center"> | |||
<math> | |||
\frac{\partial}{\partial\zeta} \biggl[ (\chi_i^2 + \zeta^2)^{-1/2} - \frac{1}{2}\chi_i^{-2} - C_\mathrm{B}^' \biggr] | |||
= -\zeta (\chi_i^2 + \zeta^2)^{-3/2} = 0 . | |||
</math> | |||
</div> | |||
For all values of <math>\chi_i</math>, this relation will be satisfied only at <math>\zeta = 0</math>. Hence, vertically, the enthalpy maximum will be located in the equatorial plane of the torus. Examining the radial enthalpy profile in the equatorial plane, we realize that the enthalpy maximum will occur where, | |||
<div align="center"> | |||
<math> | |||
\frac{\partial}{\partial\chi} \biggl[ \chi^{-1} - \frac{1}{2}\chi^{-2} - C_\mathrm{B}^' \biggr] | |||
= -\chi^{-2} + \chi^{-3} = 0 . | |||
</math> | |||
</div> | |||
This relation will be satisfied only at <math>\chi = \varpi/\varpi_0 = 1</math>. Hence, <math>\varpi_0</math> is not only the radial location (in the equatorial plane) where the angular frequency of the torus equals the Keplerian frequency, it is also the radial location of the pressure maximum. | |||
===Boundary Conditions=== | ===Boundary Conditions=== | ||
Revision as of 12:24, 8 September 2012

|
|---|
| | Tiled Menu | Tables of Content | Banner Video | Tohline Home Page | |
Massless Polytropic Tori
(aka Palapoizou-Pringle Tori)
In a seminal paper that focused on an analysis of nonaxisymmetric instabilities in accretion disks, Papaloizou & Pringle (1984, MNRAS, 208, 721-750; hereafter, PP84) began by constructing equilibrium structures of axisymmetric, polytropic tori that reside in (orbit about) a point-mass potential. The derived structures have analytic prescriptions. Although the tori constructed by PP84 were not self-gravitating — i.e., the tori were massless — it is nevertheless instructive for us to examine how these equilibrium structures were derived.
Governing Relations
As has been derived elsewhere, for axisymmetric configurations that obey a barotropic equation of state, hydrostatic balance is governed by the following algebraic expression:
<math>H + \Phi_\mathrm{eff} = C_\mathrm{B} ,</math>
where <math>C_\mathrm{B}</math> is the Bernoulli constant,
<math>\Phi_\mathrm{eff} \equiv \Phi + \Psi ,</math>
and <math>\Psi</math> is the relevant centrifugal potential. For self-gravitating configurations, this algebraic expression must be satisfied in concert with a self-consistent solution of the Poisson equation, but for the massless PP84 toroidal structures, <math>~\Phi</math> is just the Newtonian potential presented by a point-like object of mass <math>M_\mathrm{pt}</math>, namely,
<math>\Phi = - \frac{GM_\mathrm{pt}}{(\varpi^2 + z^2)^{1/2}} .</math>
Hence, the enthalpy distribution <math>H(\varpi,z)</math> throughout the torus can be described analytically for any one of a number of different simple rotation profiles by plugging the appropriate expression for the associated centrifugal potential, <math>\Psi(\varpi)</math>, into the governing relation,
<math> H = -\Phi_\mathrm{eff} + C_\mathrm{B} = \frac{GM_\mathrm{pt}}{(\varpi^2 + z^2)^{1/2}} - \Psi + C_\mathrm{B} . </math>
Supplemental Relations
Following PP84, we supplement the above-specified set of governing equations with a polytropic equation of state, as defined in our overview of supplemental relations for time-independent problems. Specifically, we will assume that <math>~\rho</math> is related to <math>~H</math> through the relation,
<math>~H = (n+1)K_\mathrm{n} \rho^{1/n}</math> ,
or we can set,
<math> H = (n+1) \frac{P}{\rho} . </math>
Inverting the first of these two expressions allows us to immediately derive the density distribution <math>\rho(\varpi,z)</math> throughout the torus from the derived algebraic expression for <math>H(\varpi,z)</math>. Different density distributions will be obtained for different selected polytropic indexes and/or for different selected functional forms of the centrifugal potential.
Here, also following PP84, we impose a steady-state velocity flow-field that is described by a fluid with uniform specific angular momentum, <math>j_0</math>. Drawing from our table of example simple rotation profiles, the centrifugal potential that describes this chosen flow-field is given by the expression,
<math> \Psi(\varpi) = \frac{j_0^2}{2\varpi^2} . </math>
Summary
Inserting the two supplemental relations into the governing algebraic expression for <math>H(\varpi,z)</math>, we conclude that the polytropic tori studied by PP84 must have structures that satisfy the equation,
<math> (n+1)\frac{P}{\rho} = \frac{GM_\mathrm{pt}}{(\varpi^2 + z^2)^{1/2}} - \frac{j_0^2}{2\varpi^2} + C_\mathrm{B} . </math>
This is identical to Eq. (2.8) of PP84.
Solution
As PP84 point out, for these toroidal structures, it is convenient to normalize all lengths to the position in the equatorial plane, <math>\varpi_0</math>, at which a fluid particle with specific angular momentum <math>j_0</math> has an angular orbital frequency, <math>\dot\varphi = j_0/\varpi^2</math>, that matches the Keplerian orbital frequency,
<math> \omega_K \equiv \biggl[ \frac{GM_\mathrm{pt}}{\varpi^3} \biggr]^{1/2} , </math>
that is associated with the point-mass, <math>M_\mathrm{pt}</math>. That is, it is convenient to define the dimensionless coordinates,
<math> \chi \equiv \frac{\varpi}{\varpi_0} ~~~~~\mathrm{and}~~~~~ \zeta \equiv \frac{z}{\varpi_0} , </math>
where,
<math> \varpi_0 \equiv \frac{j_0^2}{GM_\mathrm{pt}} . </math>
The algebraic relation defining the equilibrium structure then becomes,
<math> H = (n+1)\frac{P}{\rho} = \frac{GM_\mathrm{pt}}{\varpi_0} \biggl[ (\chi^2 + \zeta^2)^{-1/2} - \frac{1}{2}\chi^{-2} - C_\mathrm{B}^' \biggr] , </math>
where the normalized Bernoulli constant,
<math> C_\mathrm{B}^' \equiv - \frac{C_\mathrm{B} \varpi_0}{GM_\mathrm{pt}} . </math>
Pressure Maximum
It is instructive to examine at what location inside the torus the enthalpy (and density and gas pressure) assumes its maximum value. At any radial location, <math>\chi_i</math>, <math>H</math> has a vertical maximum where <math>\partial H/\partial\zeta = 0.</math> That is, the maximum occurs where,
<math> \frac{\partial}{\partial\zeta} \biggl[ (\chi_i^2 + \zeta^2)^{-1/2} - \frac{1}{2}\chi_i^{-2} - C_\mathrm{B}^' \biggr] = -\zeta (\chi_i^2 + \zeta^2)^{-3/2} = 0 . </math>
For all values of <math>\chi_i</math>, this relation will be satisfied only at <math>\zeta = 0</math>. Hence, vertically, the enthalpy maximum will be located in the equatorial plane of the torus. Examining the radial enthalpy profile in the equatorial plane, we realize that the enthalpy maximum will occur where,
<math> \frac{\partial}{\partial\chi} \biggl[ \chi^{-1} - \frac{1}{2}\chi^{-2} - C_\mathrm{B}^' \biggr] = -\chi^{-2} + \chi^{-3} = 0 . </math>
This relation will be satisfied only at <math>\chi = \varpi/\varpi_0 = 1</math>. Hence, <math>\varpi_0</math> is not only the radial location (in the equatorial plane) where the angular frequency of the torus equals the Keplerian frequency, it is also the radial location of the pressure maximum.
Boundary Conditions
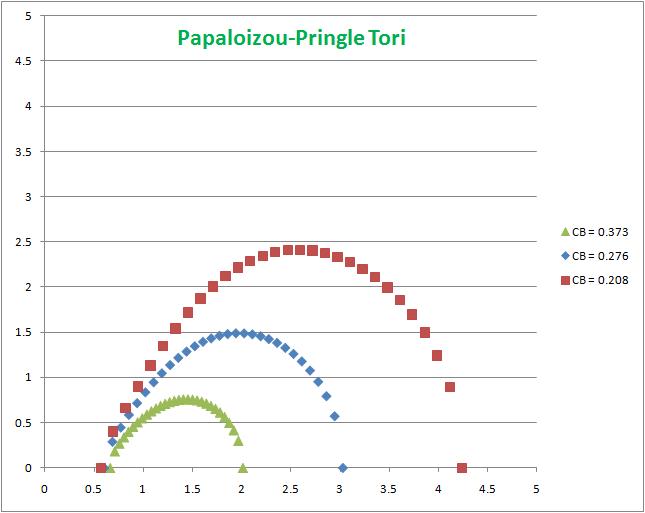
The surface of the torus occurs where the enthalpy goes to zero. The meridional <math>(\chi,\zeta)</math> cross-section through three such surfaces are displayed in the accompanying figure. The displayed surfaces correspond to <math>C_\mathrm{B}^' =</math> 0.208 (red curve), 0.276 (blue curve), and 0.373 (gold curve). Carrying forward the above discussion, we note that in all three cases the pressure maximum is located at <math>(\chi,~\zeta) = (1,~0)</math>. Properties of these tori are described in more detail in an accompanying discussion entitled, Toroidal Configurations and Related Coordinate Systems.
In the equatorial plane <math>(\zeta=0)</math>, the locations of the inner and outer edges of the torus are obtained by setting both <math>H</math> and <math>\zeta</math> to zero, that is, they are obtained from the roots of the equation,
<math> \chi^{-2} - 2\chi^{-1} + 2C_\mathrm{B}^' = 0 , </math>
that is, the inner <math>(\chi_-)</math> and outer <math>(\chi_+)</math> edges are located at,
<math> \chi_\pm = \frac{1}{1 \mp \sqrt{1-2C_\mathrm{B}^'}} . </math>
Clearly, the relative cross-sectional size — or, as defined in PP84, the dimensionless distortion parameter <math>\delta \equiv (\chi_+ + \chi_-)/2 = (2C_\mathrm{B}^')^{-1}</math> — is determined by the choice of the dimensionless Bernoulli constant, which must lie in the range, <math> 1/2 \geq C_\mathrm{B}^' \geq 0</math>. For later reference, we will also note that the ratio of the inner edge to the outer edge is,
<math> \frac{\chi_{-}}{\chi_{+}} = \frac{ 1 + \sqrt{1-2C_\mathrm{B}^'} }{1 - \sqrt{1-2C_\mathrm{B}^'} } . </math>
We should perhaps emphasize that the shape of the surface of each torus, as shown in the accompanying figure, is independent of the chosen polytropic index.
Hachisu Self-Consistent Field Technique
For the sake of contextual continuity, it is useful to relate the above result to the Hachisu self-consistent field (HSCF) technique, which we rely upon heavily to derive the equilibrium structure of self-gravitating systems. The HSCF technique begins by identifying the relevant algebraic expression for the enthalpy as derived above, namely,
<math> H = \frac{GM_\mathrm{pt}}{(\varpi^2 + z^2)^{1/2}} - \frac{j_0^2}{2\varpi^2} + C_\mathrm{B} . </math>
In the HSCF technique, it is customary to normalize all lengths to the distance <math>\varpi_{+}</math> from the origin to the point where the outer edge of the torus touches the equatorial plane. From this perspective, then, the relevant dimensionless coordinates are,
<math> x_\mathrm{HSCF} \equiv \frac{\varpi}{\varpi_{+}} ~~~~~\mathrm{and}~~~~~ z_\mathrm{HSCF} \equiv \frac{z}{\varpi_{+}} , </math>
and the equation for the dimensionless enthalpy becomes,
<math> H_\mathrm{HSCF} \equiv \frac{H}{(GM_\mathrm{pt}/\varpi_{+})} = (x_\mathrm{HSCF}^2 + z_\mathrm{HSCF}^2)^{-1/2} - \frac{1}{2} (j_\mathrm{HSCF}^2) x_\mathrm{HSCF}^{-2} - C_\mathrm{HSCF} , </math>
where the normalized Bernoulli constant,
<math> C_\mathrm{HSCF} \equiv - \frac{C_\mathrm{B} \varpi_{+}}{GM_\mathrm{pt}} , </math>
and the normalized specific angular momentum is,
<math> j_\mathrm{HSCF} \equiv \frac{j_0}{(GM_\mathrm{pt} \varpi_{+})^{1/2}} . </math>
This expression for the dimensionless enthalpy has two unknowns: <math>j_\mathrm{HSCF}</math> and <math>C_\mathrm{HSCF}</math>. Hence, two boundary points must be specified before a solution for <math>H_\mathrm{HSCF}(\varpi,z)</math> can be obtained. In the HSCF technique, it is customary to specify the location of two points on the surface of the configuration, where by design <math>H=0</math>. For toroidal configurations, it is furthermore customary for that specification to be where the inner and outer edges of the torus touch the equatorial plane. By design, the outer edge is at <math>(x_\mathrm{HSCF}, ~z_\mathrm{HSCF}) = (1, ~0)</math>; the inner edge will be at <math>(x_\mathrm{HSCF}, ~z_\mathrm{HSCF}) = (x_{in}, ~0)</math>. Setting <math>H_\mathrm{HSCF}=0</math> at both of these locations gives the following two algebraic relations,
<math> C_\mathrm{HSCF} = 1 - \frac{1}{2} (j_\mathrm{HSCF}^2) , </math>
and
<math> C_\mathrm{HSCF} = x_{in}^{-1} - \frac{1}{2} (j_\mathrm{HSCF}^2) x_{in}^{-2} , </math>
which can be used in combination to solve for the two unknowns. The result is,
<math> C_\mathrm{HSCF} = \frac{1}{1 + x_{in}} , </math>
and,
<math> j_\mathrm{HSCF} = \biggl[ \frac{2x_{in}}{1 + x_{in}} \biggr]^{1/2} . </math>
At what radial position in the equatorial plane, <math>x_0</math>, is the pressure maximum located? The pressure maximum is also the enthalpy maximum, so the answer is given by looking in the equatorial plane <math>(z_\mathrm{HSCF} = 0)</math> for the location where <math>dH_\mathrm{HSCF}/dx_\mathrm{HSCF} = 0</math>. Since,
<math> \frac{dH_\mathrm{HSCF}}{dx_\mathrm{HSCF}} = - x_\mathrm{HSCF}^{-2} + (j_\mathrm{HSCF}^2) x_\mathrm{HSCF}^{-3} \, , </math>
the pressure maximum must be located at,
<math> x_\mathrm{HSCF} = x_0 = j_\mathrm{HSCF}^2 \, . </math>
Hence, in terms of <math>x_{in}</math>,
<math> x_0 = \frac{2x_{in}}{1 + x_{in}} . </math>
Comparison
The solution derived by PP84 (presented above) is normalized such that the pressure maximum is always in the equatorial plane at radial coordinate <math>\chi = 1</math>, and tori of different thicknesses are constructed by specifying different values of the dimensionless Bernoulli constant, <math>C_\mathrm{B}^'</math>. Using the HSCF approach, the position of the outer edge of the torus is fixed and tori of different thicknesses are selected by moving the inner edge, <math>x_{in}</math>, around. In order to examine whether or not the two solutions are, in fact, the same, we will re-write the expression given above for <math>\chi_{-}/\chi_{+}</math> in terms of <math>x_{in}</math>. In order to do this, we need to convert <math>C_\mathrm{HSCF}</math> to <math>C_\mathrm{B}^'</math>. Based on their definitions, the ratio
<math> \frac{C_\mathrm{B}^'}{C_\mathrm{HSCF} } = \frac{\varpi_0}{\varpi_{+}} = x_0 . </math>
Hence,
<math> C_\mathrm{B}^' = x_0~C_\mathrm{HSCF} = \biggl( \frac{2x_{in}}{1+x_{in}} \biggr) \biggl( \frac{1}{1+x_{in}} \biggr) = \frac{2x_{in}}{(1+x_{in})^2}. </math>
Therefore,
<math> 1 - 2C_\mathrm{B}^' = 1 - \frac{4x_{in}}{(1+x_{in})^2} = \frac{ (1+x_{in})^2 - 4x_{in} }{(1+x_{in})^2} = \frac{ (1-x_{in})^2 }{(1+x_{in})^2} \, , </math>
and,
<math> \frac{\chi_{-}}{\chi_{+}} = \frac{ 1 + \sqrt{1-2C_\mathrm{B}^'} }{1 - \sqrt{1-2C_\mathrm{B}^'} } = \frac{ 1 + \frac{1-x_{in}}{1+x_{in}} }{1 - \frac{1-x_{in}}{1+x_{in}}} = . </math>
Related Wikipedia Discussions

|
|---|
|
© 2014 - 2021 by Joel E. Tohline |