Difference between revisions of "User:Tohline/ThreeDimensionalConfigurations/ChallengesPt5"
| Line 211: | Line 211: | ||
This subsection borrows heavily from [[User:Tohline/ThreeDimensionalConfigurations/ChallengesPt4#Step4|an accompanying discussion]]. | This subsection borrows heavily from [[User:Tohline/ThreeDimensionalConfigurations/ChallengesPt4#Step4|an accompanying discussion]]. | ||
===Old Way of Thinking=== | |||
It seems reasonable to assume that this ''off-center ellipse'' expression will properly describe the orbital path of various Lagrangian fluid elements that make up the uniform-density ellipsoid. Assuming that, when viewed from the rotating-and-tipped coordinate frame, each fluid element's motion along this trajectory is oscillatory, it is reasonable to assume that the time-dependent x'-y' coordinate position of each fluid element is given by the expressions, | It seems reasonable to assume that this ''off-center ellipse'' expression will properly describe the orbital path of various Lagrangian fluid elements that make up the uniform-density ellipsoid. Assuming that, when viewed from the rotating-and-tipped coordinate frame, each fluid element's motion along this trajectory is oscillatory, it is reasonable to assume that the time-dependent x'-y' coordinate position of each fluid element is given by the expressions, | ||
<table border="0" cellpadding="5" align="center"> | <table border="0" cellpadding="5" align="center"> | ||
| Line 293: | Line 294: | ||
\boldsymbol{\hat\jmath'} \biggl[ x' \biggl( \frac{y'_\mathrm{surf}}{x_\mathrm{surf}}\biggr) \dot\varphi \biggr] \, . | \boldsymbol{\hat\jmath'} \biggl[ x' \biggl( \frac{y'_\mathrm{surf}}{x_\mathrm{surf}}\biggr) \dot\varphi \biggr] \, . | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
===New Thoughts=== | |||
Suppose the frequency of oscillation in the x' Lagrangian coordinate is twice the frequency of oscillation in the y' Lagrangian coordinate. Then we have, | |||
<table border="0" cellpadding="5" align="center"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td align="right"> | |||
<math>~x'</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="center"> | |||
<math>~=</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="left"> | |||
<math>~x_\mathrm{surf}\cos(2 \dot\varphi t)</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="center"> and, | |||
<td align="right"> | |||
<math>~y' - y'_\mathrm{center}</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="center"> | |||
<math>~=</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="left"> | |||
<math>~y'_\mathrm{surf}\sin(\dot\varphi t) \, .</math> | |||
</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
In this case, as viewed from the rotating-and-tipped coordinate frame, the corresponding velocity components are, | |||
<table border="0" cellpadding="5" align="center"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td align="right"> | |||
<math>~\dot{x}'</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="center"> | |||
<math>~=</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="left"> | |||
<math>~- 2x_\mathrm{surf}~ \dot\varphi \cdot \sin(2 \dot\varphi t) = 2(y'_\mathrm{center} - y') \biggl[ \frac{x_\mathrm{surf}}{y'_\mathrm{surf}} \biggr] \dot\varphi </math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="center"> and, | |||
<td align="right"> | |||
<math>~\dot{y}' </math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="center"> | |||
<math>~=</math> | |||
</td> | |||
<td align="left"> | |||
<math>~y'_\mathrm{surf}~\dot\varphi \cdot \cos(\dot\varphi t) = x' \biggl[ \frac{y'_\mathrm{surf}}{x_\mathrm{surf}}\biggr] \dot\varphi \, .</math> | |||
</td> | </td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
Revision as of 20:56, 13 May 2021
Challenges Constructing Ellipsoidal-Like Configurations (Pt. 5)
This chapter extends the accompanying chapters titled, Construction Challenges (Pt. 1), (Pt. 2), (Pt. 3), and (Pt. 4).

|
|---|
| | Tiled Menu | Tables of Content | Banner Video | Tohline Home Page | |
Tilted Plane Intersects Ellipsoid
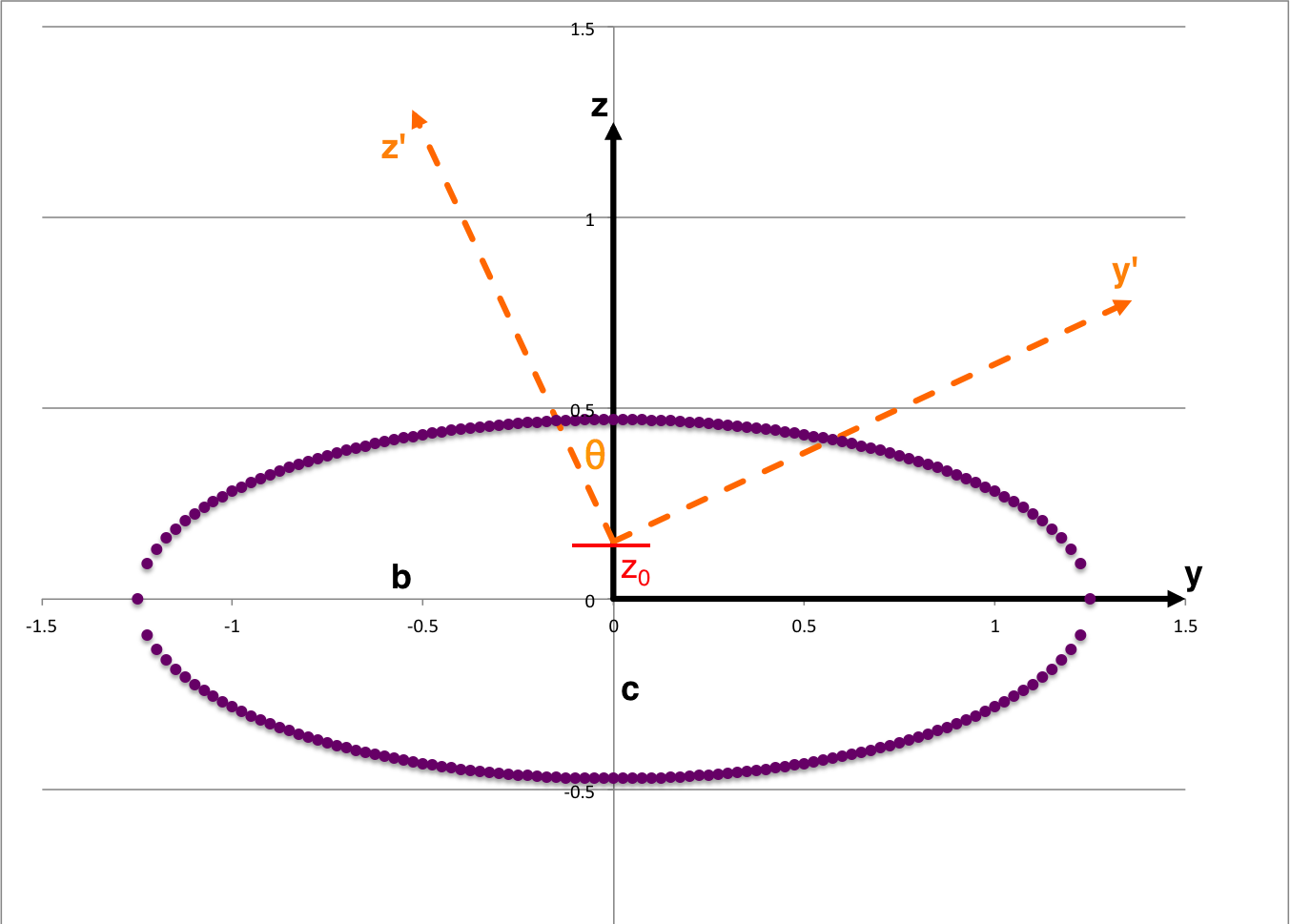
In a an early subsection of the accompanying discussion, we have pointed out that the intersection of each Lagrangian fluid element's tipped orbital plane with the surface of the (purple) ellipsoidal surface is given by the (unprimed) body-frame coordinates that simultaneously satisfy the expressions,
|
<math>~1</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~\biggl( \frac{x}{a}\biggr)^2 + \biggl( \frac{y}{b}\biggr)^2 + \biggl( \frac{z}{c}\biggr)^2 </math> |
and, |
<math>~z</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~y \tan\theta + z_0 \, ,</math> |
where z0 is the location where the tipped plane intersects the z-axis of the body frame. Combining these two expressions, we see that an intersection between the tipped plane and the ellipsoidal surface will occur at (x, y)-coordinate pairs that satisfy what we will henceforth refer to as the,
| Intersection Expression | ||
|
<math>~1 - \frac{x^2}{a^2} </math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~y^2 \biggl[\frac{c^2 + b^2\tan^2\theta}{b^2c^2} \biggr] + y \biggl[ \frac{2z_0 \tan\theta}{c^2} \biggr] + \frac{z_0^2}{c^2} \, , </math> |
as long as z0 lies within the range,
|
<math>~z_0^2</math> |
<math>~\le</math> |
<math>~c^2 + b^2\tan^2\theta \, .</math> |
Before calling upon any of Riemann's model parameters, from geometric considerations alone we should be able to determine exactly what the expression is for any off-center ellipse that results from slicing — at a tipped angle — the chosen ellipsoid.
In the equatorial plane of the tipped coordinate system — that is, after mapping <math>~x \rightarrow x'</math> and <math>~y \rightarrow (y' \cos\theta - z'\sin\theta)</math>, then setting <math>~z' = 0</math> — this intersection expression becomes,
|
<math>~x'</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~a \biggl\{ 1 - \biggl[ (y'\cos\theta)^2 \biggl( \frac{c^2 + b^2\tan^2\theta}{b^2c^2} \biggr) + y'\cos\theta \biggl( \frac{2z_0 \tan\theta}{c^2} \biggr) + \frac{z_0^2}{c^2} \biggr] \biggr\}^{1 / 2}</math> |
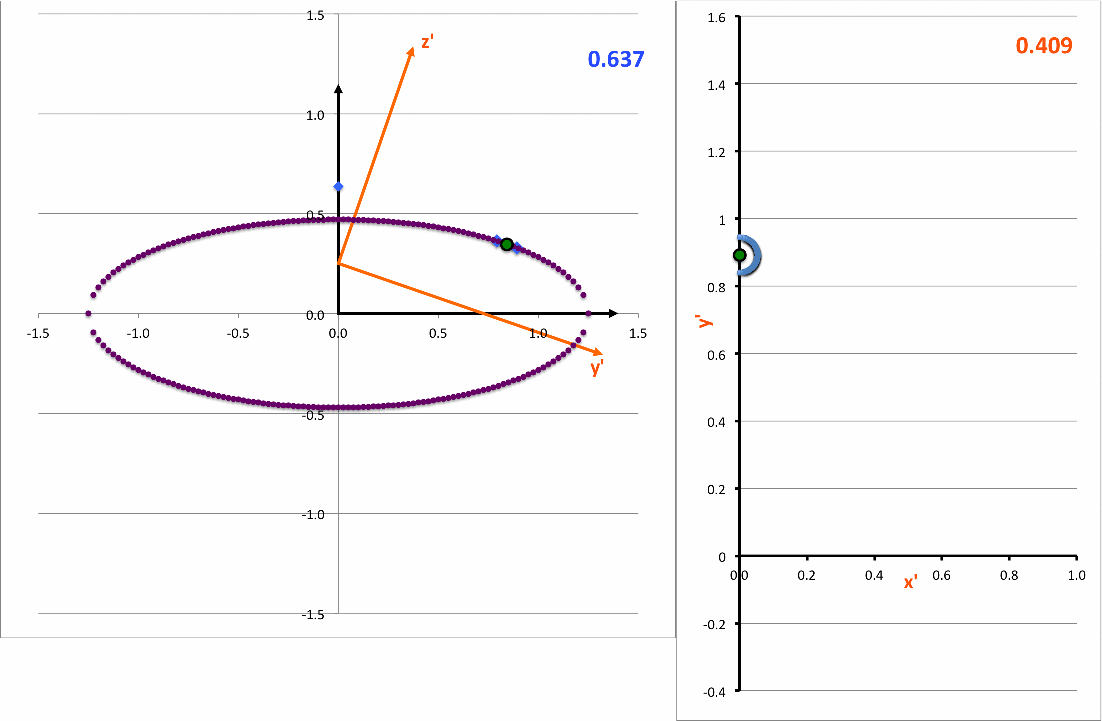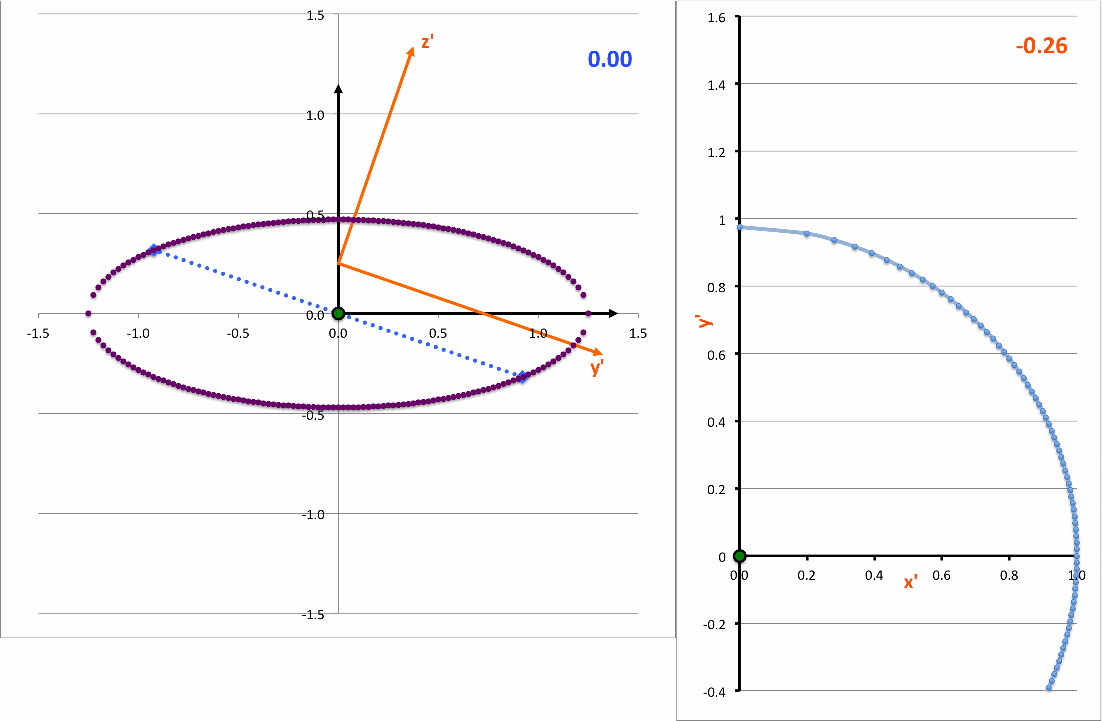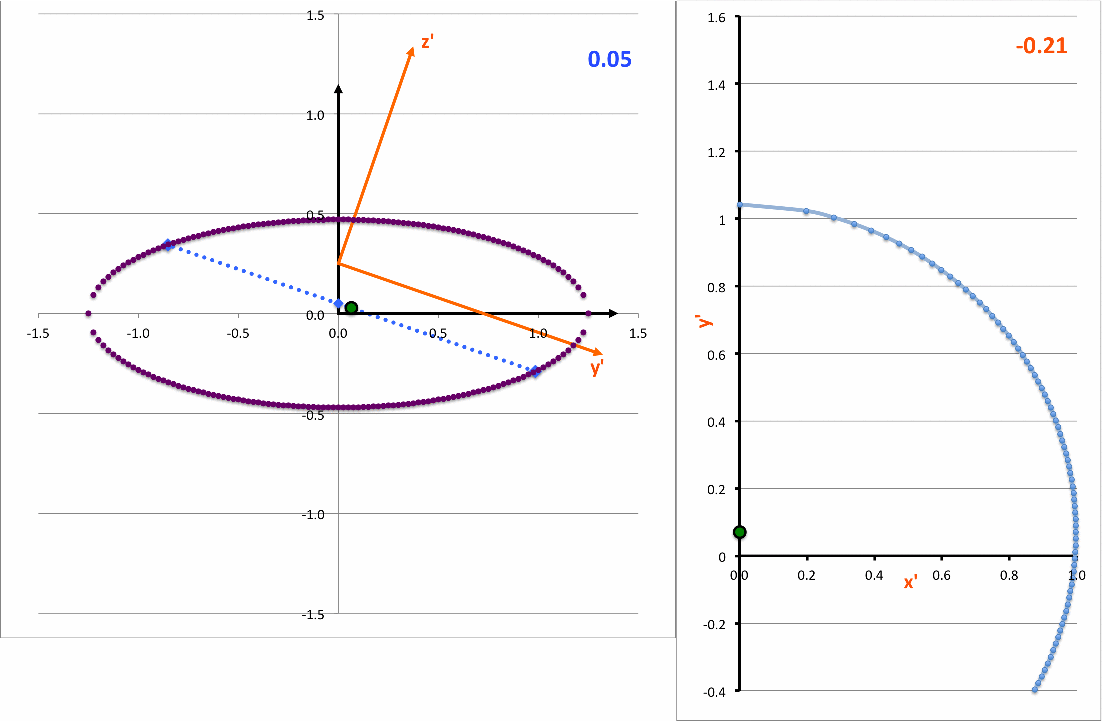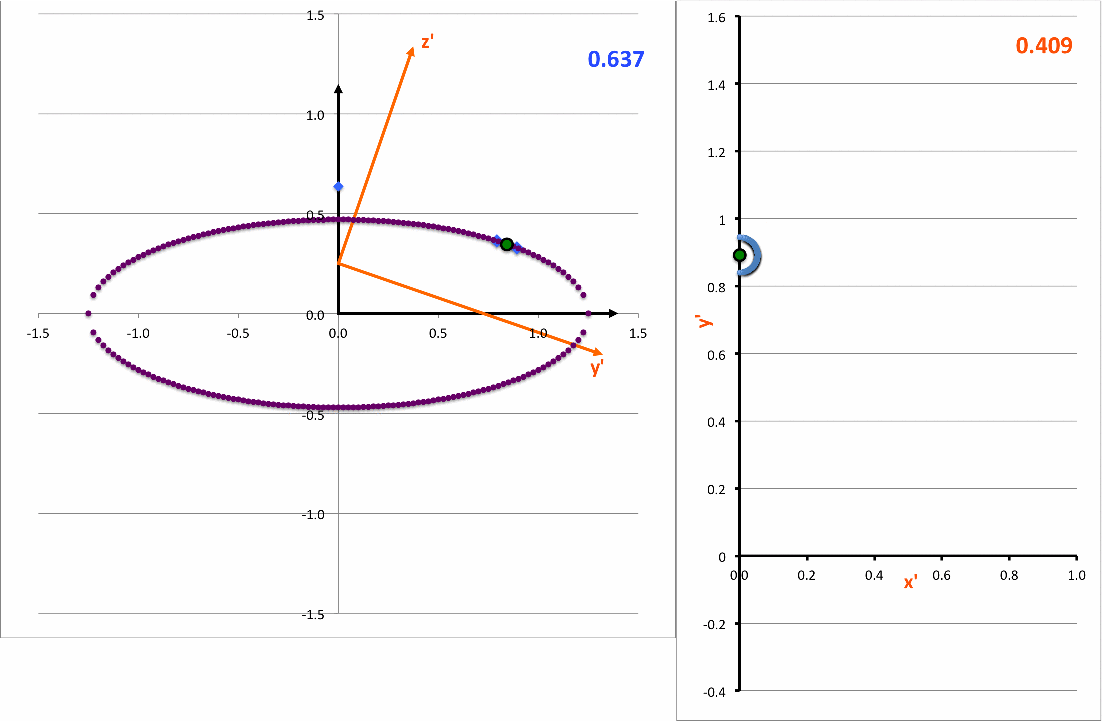
The light-blue curve in the right-hand panel of the following animation is a plot of this <math>~x'(y')</math>function for various values of <math>~z_0</math> (as indicated by the light-blue numerical value in the upper-right corner of the figure's left-hand panel.
As it turns out — see our accompanying discussion — this expression can be rewritten as,
|
<math>~1</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \biggl[\frac{x'}{x_\mathrm{surf}} \biggr]^2 + \biggl[ \frac{(y' - y'_\mathrm{center} ) }{y'_\mathrm{surf}} \biggr]^2 \, , </math> |
demonstrating that, as viewed from the x'-y' plane, the (light-blue) intersection curve is always an off-center ellipse. See also our COLLADA-based representation of these curves.
Trajectory of Lagrangian Fluid Elements
This subsection borrows heavily from an accompanying discussion.
Old Way of Thinking
It seems reasonable to assume that this off-center ellipse expression will properly describe the orbital path of various Lagrangian fluid elements that make up the uniform-density ellipsoid. Assuming that, when viewed from the rotating-and-tipped coordinate frame, each fluid element's motion along this trajectory is oscillatory, it is reasonable to assume that the time-dependent x'-y' coordinate position of each fluid element is given by the expressions,
|
<math>~x'</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~x_\mathrm{surf}\cos(\dot\varphi t)</math> |
and, |
<math>~y' - y'_\mathrm{center}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~y'_\mathrm{surf}\sin(\dot\varphi t) \, .</math> |
In this case, as viewed from the rotating-and-tipped coordinate frame, the corresponding velocity components are,
|
<math>~\dot{x}'</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~- x_\mathrm{surf}~ \dot\varphi \cdot \sin(\dot\varphi t) = (y'_\mathrm{center} - y') \biggl[ \frac{x_\mathrm{surf}}{y'_\mathrm{surf}} \biggr] \dot\varphi </math> |
and, |
<math>~\dot{y}' </math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~y'_\mathrm{surf}~\dot\varphi \cdot \cos(\dot\varphi t) = x' \biggl[ \frac{y'_\mathrm{surf}}{x_\mathrm{surf}}\biggr] \dot\varphi \, .</math> |
This means that the (dimensional) velocity vector is,
|
<math>~\boldsymbol{u'}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \boldsymbol{\hat\imath'} \dot{x}' + \boldsymbol{\hat\jmath'} \dot{y}' </math> |
|
|
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~ \boldsymbol{\hat\imath'} \biggl[ (y'_\mathrm{center} - y') \biggl( \frac{x_\mathrm{surf}}{y'_\mathrm{surf}} \biggr) \dot\varphi \biggr] + \boldsymbol{\hat\jmath'} \biggl[ x' \biggl( \frac{y'_\mathrm{surf}}{x_\mathrm{surf}}\biggr) \dot\varphi \biggr] \, . </math> |
New Thoughts
Suppose the frequency of oscillation in the x' Lagrangian coordinate is twice the frequency of oscillation in the y' Lagrangian coordinate. Then we have,
|
<math>~x'</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~x_\mathrm{surf}\cos(2 \dot\varphi t)</math> |
and, |
<math>~y' - y'_\mathrm{center}</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~y'_\mathrm{surf}\sin(\dot\varphi t) \, .</math> |
In this case, as viewed from the rotating-and-tipped coordinate frame, the corresponding velocity components are,
|
<math>~\dot{x}'</math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~- 2x_\mathrm{surf}~ \dot\varphi \cdot \sin(2 \dot\varphi t) = 2(y'_\mathrm{center} - y') \biggl[ \frac{x_\mathrm{surf}}{y'_\mathrm{surf}} \biggr] \dot\varphi </math> |
and, |
<math>~\dot{y}' </math> |
<math>~=</math> |
<math>~y'_\mathrm{surf}~\dot\varphi \cdot \cos(\dot\varphi t) = x' \biggl[ \frac{y'_\mathrm{surf}}{x_\mathrm{surf}}\biggr] \dot\varphi \, .</math> |
See Also
- Riemann Type 1 Ellipsoids
- Construction Challenges (Pt. 1)
- Construction Challenges (Pt. 2)
- Construction Challenges (Pt. 3)
- Construction Challenges (Pt. 4)
- Construction Challenges (Pt. 5)
- Related discussions of models viewed from a rotating reference frame:
- PGE
- NOTE to Eric Hirschmann & David Neilsen... I have moved the earlier contents of this page to a new Wiki location called Compressible Riemann Ellipsoids.

|
|---|
|
© 2014 - 2021 by Joel E. Tohline |